Computer vision is the field of study that explores the ways of teaching computers to see the world like us. To train computers to eye objects and people, identify, and process images and video content, engineers use a set of technologies and methods. Among high tech to be put on the list are image recognition and processing, pattern recognition, visual search, object recognition, scene reconstruction, and more. And what constitutes the basis for all the aforementioned is machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL).
ML has enabled computers to have good enough eyesight. Now, computer vision finds applications across various business areas. The first example that comes to mind is top-notch surveillance systems. However, such usage of technology is a matter of heated debates over privacy issues and tightening control.
But beyond that, computer vision enhances and transforms the media and entertainment industry. That involves visual media, including TV and film production, interactive media, games, sports, advertising, and gamified customer experience.
Augmented Intelligence: AR, VR, MR
Augmented intelligence is a model of cooperation between humans and AI, which results in better performance, improved decision-making, and new options for solving traditional tasks unleashed. According to Gartner’s Hype Cycle For AI, 2019, augmented intelligence is the result of companies scaling AI across different business workflows. It is a more general notion that encompasses augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR).

Source: Unsplash
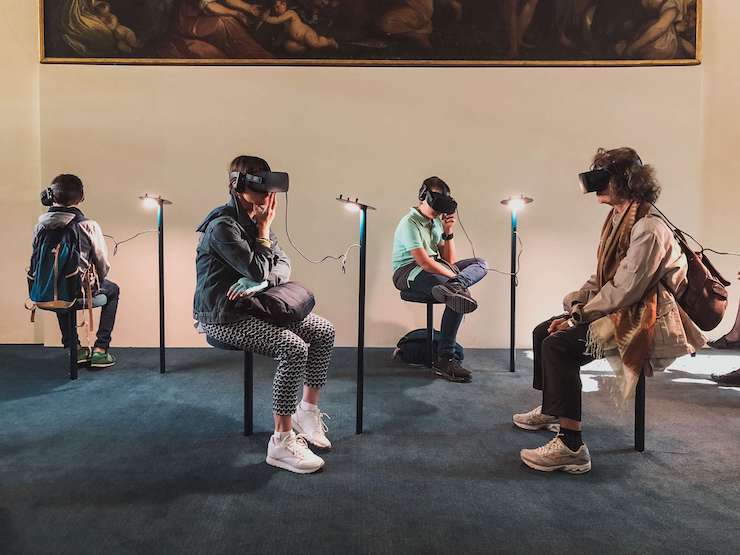
The evolution of immersive virtual reality environments and related hardware made new terms to proliferate. Today, different ML-based “realities” enables users to interact with virtual objects in a distinct manner.
Virtual Reality (VR) completely separates users from sounds and voices in the surrounding reality, namely real reality. Users gain an unlimited place for actions.
Today, among the most cutting-edge VR gear are Oculus Rift, Samsung Gear VR, and HTC Vive. These solutions help users indulge themselves in new realities. With a wave of the hand, they can augment the surrounding environment with works of art from VR libraries or get a taste of immersive gaming experience.
Augmented Reality (AR) allows filling in real reality with virtual images, objects, animation, visual effects, captions, and so forth. Such are AR-driven model applications like Pokémon GO, Snapchat, Google Glass, and more. This technology powers such solutions as AR Mirror to provide mesmerizing customer experience, or Smart Glasses as seen solely in movies just a little while ago, or make such captivating sport as drone racing possible. We are going to dwell upon these applications of AR later in our article.
Mixed Reality (MR) is pretty similar to AR. But instead of building text and images in the reality that surrounds a user, MR enables creating virtual objects as if they are already present in the room, each in its place. For instance, Microsoft HoloLens allows users to see one another in a virtual environment that an HMD display broadcasts to a user.
Computer vision plays a pivotal role in making augmented intelligence possible and bringing games and customer experience to a brand-new level. Share on XSmart Glasses
Both hardware capabilities and the leap in machine learning gave an impetus to developing AR headsets. Such are new Glass by Google announced recently. This high-end gear is powered by Qualcomm’s Snapdragon XR1 chip, designed specifically for augmented intelligence.
Glass is first and foremost a business-oriented solution. Professionals across different industries can exploit it to boost the production quality, reduce time to market and overall costs.
A competitor’s product is Microsoft HoloLens, a mixed reality device primarily developed for industrial uses. The solution can be utilized not only in entertainment. For instance, Ford employs mixed reality for designing cars. Also, the smart solution can serve the needs of healthcare specialists, military objectives, or consumers in brick-and-mortar stores.
Computer Vision in Interactive Media
With the advent of AR, digital media progresses towards more and more interactive content. Traditional TV and radio don’t require consumers to participate. Interactive media provides a whole new user experience by offering such elements as moving images and graphics, animation, digital captions, video, and audio. Consumers can command all these elements by using controllers, be it a smartphone, video game controller, or Google Glass, or other eyewear.
AR renovates media applications by enabling an immersive experience. At its simplest, AR solutions let users communicate with people they normally can’t get in touch with. And in a more complex alternative, it breathes life into new worlds that are almost carbon copies of the reality but filled with virtual objects and virtual opportunities.
The amazing experience becomes possible due to the combination of a real-time camera video source with image synthesis. As a result, the physical world receives interactive graphic overlays, which enables AR.
Along with entertaining consumers, interactive media can be applied in education to help ensure the smart process of learning or in museums to let visitors plunge into virtual trips and get extra information on museum pieces.
The Sport of the Future: Drone Racing
Flying drones has gained a lot of hype lately. There is already the Drone Racing League (DRL) actively engage in developing racing drones, organizing professional tournaments, and turning AR-based entertainment into the sport that blurs the line between what is real and what is digital.
A human pilot of a racing drone wears an AR headset. It enables the first-person view and displays a race track, the drone’s video feed, and fight statistics. But soon, drones can start racing by themselves.
Like in a range of games where humans pitted themselves against AI and lost, computers are going to defeat human pilots in drone racing. So, a fully autonomous robot RacerAI has four cameras to collect visual data, detect and classify objects with twice the field of view as human pilots. This racing drone programmed for autonomous flying is predicted to beat human competitors by 2023.
Every drone is an edge device, in which AI inference takes place close to the data source. That allows better data processing speed and independence of hardware restrictions for data exchange. You can find out more about AI at the edge in the previous article by InData Labs.
More Applications of Сomputer Vision in Media
Driven by computer vision, media experience is heading towards new milestones. Watson Media by IBM allows sports fans to capture match highlights automatically and share them across social media. AI enables a set of solutions that allows collecting and analyzing video content and images, as mediated by computer vision, or users’ language and sentiment information.
For marketers, who monitor brand exposure during sports events, computer vision offers a range of video data analysis capabilities. It would be impossible to manually process all the raw video content that comes from multiple sports venues. Custom computer vision solutions can help tackle massive amounts of content, track logos across various media platforms and broadcasting channels, and calculate the value of every case of exposure.

Source: Unsplash
One more perk that computer vision offers is assisting consumers in finding where they can buy some stuff they see on screen. TheTake.AI understands videos and makes it possible to detect fashion items, jewelry, equipment, and more to search for buying opportunities across the web. Now, if you see a favorite character wearing a stunning look, you can automatically figure out where you can get the same one for yourself.
Computer vision also allows marketers to grasp the real reactions of consumers to the content. Popular AI-enabled sentiment analysis helps process text feedback and elicit positive, negative, or neutral emotions. Computer vision assists brands with watching users, measuring a so-called actual eyes-on-screen attention, tracking facial expressions, and eye movement. Technology can help turn non-verbal signs into valuable data to be used to estimate consumer involvement and behavior to improve user experience.
Tacking Stock
Computer vision has paved the way for the emergence of augmented intelligence that, in turn, has enabled consumers to create virtual realities full of options unheard of previously. It is intriguing and captivating as technologies make something imaginary come true.
Today we can witness applications of computer vision infiltrating our day-to-day life and changing the ways we interact with the world. Machine learning and deep learning technologies have given rise to a new wave of computer vision uses. Some of them are on every business’s A-list: face recognition and surveillance, robots for production lines, or optimization of verification processes. And while the media and entertainment industry gains less coverage in relation to computer vision, this business area keeps up with technology innovations to thrive and grow.
In our blog, we talked about what computer vision is, how visual search works, and the role of deep learning in image recognition. You are welcome to dive into the topic to grasp a more comprehensive picture of computer vision.
Start Your Computer Vision Project with InData Labs
At InData Labs, we provide computer vision consulting and custom software development services. Our firm is here to become your strategic partner. We help our clients implement custom computer vision solutions in line with the specific requirements to serve a variety of business goals. We marry our solutions led by cutting-edge technologies to businesses in different niches.