In today’s digitized medical landscape, effective treatment and better outcomes for patients depend on the smart use of medical data. Healthcare data management treats data as a powerful asset and improves health services.
The rise of EHR/EMR systems also promotes more effective handling of patient data. Thus, over half of the surveyed US patients have an electronic health record (EHR). Moreover, over 40% have access to their patient data. This practice leads to the more effective involvement of patients in medical services.

Source: Unsplash
Therefore, the digitization of healthcare highlights the need for accurate healthcare data analytics and management. The volume and velocity of Big data development leave no chance for traditional data processing. Instead, tech-savvy data management approaches enter the fray. And this is when the subject of our research comes on stage.
In this post, we’ll talk about data management in the healthcare industry. In particular, we’ll highlight its advantages and importance for patient treatment.
What is healthcare data management?
Medical data management is the systematic organization of digital health data. This might range from electronic health records to invoices and provider information.
It allows medical providers to combine and process medical data. A combination of accurate insights, in turn, improves patient care. Moreover, it enables a more holistic view of a patient’s condition. Personalized treatment and more transparency are also the results of record handling. Keeping track of information also augurs patient safety.
But mastering data management in healthcare is a challenging task. First, medical records present a wide ecosystem of information rooted in different fields.
Thus, health information exists in forms like:

Data life cycle management in healthcare involves processing both structured and unstructured data. The former comes in a standardized format and can flow between health information systems. An example of such a type is demographics or physical characteristics like height.
Unstructured data has no predefined structure and comes in many forms. Examples of unstructured data range from images and text files, such as PDF documents. Video and audio files are also common in clinical pathways.
The problem with this type of information is that traditional methods and tools fall flat to analyze and process it. That is why machine learning and healthcare become a viable combo to process a good deal of information.
Importance of data management in healthcare
The effective use of Big data for business allows companies to reap benefits. This ranges from increased benefits to better decision-making and customer experience. How is the medical industry different? The truth is that this sector is no different. Healthcare desperately needs organizing sporadic data assets, since the stakes are high.
Source: Unsplash
Data management in the healthcare industry yields notable benefits for all sides of medical services. Benefits of data management in healthcare include:
- Rendering a holistic view of patient groups. Comprehensive medical profiles contain exhaustive information on demographics, physical characteristics, and health conditions.
- Promoting patient engagement. Personalized care for patients becomes easier through notifications and reminders. Predictive analytics solutions also allow delivering tailored offers.
- Improve health outcomes. Hospitals can track patients between visits, combating emerging health issues by suggesting proactive measures. The precision medicine approach is made possible by considering individual variability.
- Better business and clinical decision-making. It aids healthcare providers in making well-founded decisions on facility equipment and medical staff. Record handling also provides a point-of-care reference for urgent conditions.
- Check medical performance. Hospitals can analyze the quality of diagnosis and patient outcomes. These insights help achieve higher customer satisfaction and loyalty. They also keep physicians in sync with the goals of the healthcare facility.
Why is mastering data management in healthcare so hard?
But healthcare and technology haven’t always complimented each other. The adoption rates of digital records are still slow. Hence, lots of medical information is still to be digitized. But why is it taking us so slow in the modern tech-driven world?
Let’s have a look at common challenges that hamper healthcare digitization.
Fragmented records
Every year, the healthcare system generates about a zettabyte of data. This number continues to grow. The scale and dispersed nature of records pose a significant barrier to mastering Big data management in healthcare. Medical records can come in pixels, CSV, photometric interpretation, metadata, video, and others.
Moreover, duplicates also plague this industry. Records get stored in various formats by healthcare providers, insurance companies, and patients. Thus, the medical industry has no single source of truth. This makes data processing more difficult. Also, it slows down introducing machine and computer vision solutions for better treatment.
Ever-changing records
Both physicians and patients can change their names, move, or retire. The adoption of new treatments and medications also alters service delivery and data collection. That is why maintaining accurate information throughout the entire system is almost impossible. Information gaps impact patient experience and the viability of a provider’s business. As a result, treatment and clinical choices are not as effective as they could be.
Privacy and security regulations
Since 2009, over 3,700 healthcare data breaches have been reported to the HHS’ Office for Civil Rights. Hence, the sensitive nature of patient medical information is another surface for leaks. That is why governments impose strict regulations on all healthcare data. Examples of regulatory requirements include HIPAA, GDPR, and others. Thus, besides organizing data, healthcare providers have to perform the required audits and meet regulatory requirements.

Source: Unsplash
Data management process in healthcare
Paying due diligence to the digital ecosystem in medicine doesn’t boil down to one step. Instead, to tool an effective data strategy, providers must go through five key steps. These steps help better understand the question ‘What is healthcare data management for medicine providers.
Data governance
Data governance is different for each business. In general, it is a full-scale strategy to manage your information assets. During this stage, healthcare providers define specific governance practices to achieve their goals. The latter assists healthcare organizations in attaining a standardized and structured method of sharing medical data. In plain words, it is like laying the strategic background before taking actual steps.
Besides, this stage results in:
- Established internal rules for the use of data;
- Articulated value of data;
- Implemented compliance requirements;
- Improved internal and external communications.
Data integration
Next goes the process of combining scattered information from different sources into a single, unified view. The integration process is among the biggest challenges in the medical industry. EHRs, lab results, invoices, and claims create disorganized chaos of incoming information. That is why it’s hard to reconcile it all.
Source: Unsplash
Moreover, the Interoperability and Patient Access final rule makes this step paramount for your data strategy. Also, all data should abide by HIPAA 5010 and ICD-10.
Data quality management in healthcare is also important for predictive analytics in healthcare. Thus, the integrated dataset can be loaded into an analytics platform for further insights.
Data Enrichment
This stage refers to the process of supplementing raw data with new information. The latter is not present in the available datasets but is needed for qualitative analysis. This information can be found internally or externally.
Internal enrichment does not involve any third-party input. It usually means obtaining and incorporating useful information that is not available on-site. But it can be obtained through the manipulation of existing data. External enrichment involves third-party information. The latter may include records like insurance claims, lab tests, and others.
Data Storage
The information gets safely stored on the cloud or on-premise storage. This process is yet another challenge for healthcare providers. Storing clinical data must be HIPAA-compliant and easy for authorized users to access. So, the right storage option is a paramount consideration for medical facilities. Also, piecing together legacy systems while integrating new systems into the infrastructure further hampers effective digitalization.

Source: Unsplash
Predictive analytics
Once providers have a full-scale IT infrastructure, they can tap into the data to generate meaningful insights. This wealth of information goes into predictive analytics solutions. The latter is a combination of modeling, data mining, statistics, and artificial intelligence that helps predict future outcomes.
Predictive analytics healthcare examples include:
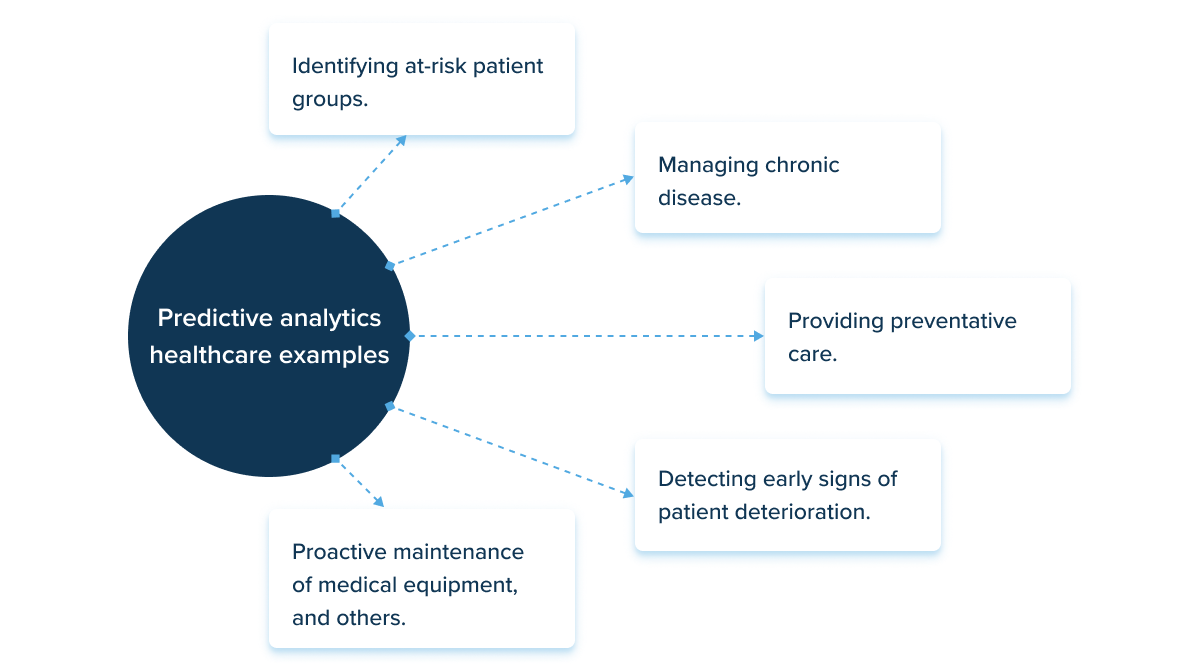
Moreover, data analysis for healthcare management augments business intelligence in medicine. Thus, healthcare marketers can amplify their decision-making process by implementing insights from patterns and correlations found in healthcare data. If you know the exact needs or preferences of your consumers, it’s easier to keep patients engaged and loyal to your healthcare facility or insurance plan.
Storage Options For Healthcare Data
The volume of medical information equated to over 2,300 exabytes in 2020. Therefore, accurate record-keeping is an important step in implementing a holistic data management strategy. Unlike paper notes, digitized medical records depend on computerized storage systems for archival of health information.
However, secure storage is challenging to achieve. Today, the combination of the edge and private and public cloud environments is the go-to storage method for medical information. Although this option doesn’t eliminate storage challenges, it helps meet the following requirements.
Scalability
The advent of medical data will increase as more technology gets introduced into the industry and the need for digital services grows. That is why storage options should present a dynamically scalable architecture. This will prove the set-up for the future and help cope with a growing amount of unstructured healthcare data.
Source: Unsplash
Compliance
The privacy rule of HIPAA requires organizations to ensure the secure handling of sensitive data. Internal audits, checksums, message authentication, or digital signatures are just some of the ways to comply with regulations.
Availability and performance
Storage options should also ensure timely access to healthcare records. Hence, storage models should amplify both performance, security, and mutability.
Support for long retention and migration
Some regulations mandate long retention periods for specific types of healthcare records. In case of server failure or technological updates, the system must provide verifiable migration paths.
Best practices for healthcare data management
Adopting a wholesome data management strategy is vital to guarantee the efficient storage and transfer of patient information. Not only will it assist healthcare professionals in making sense of all the data gathered within their facilities, but it will also benefit the entire healthcare community on a worldwide scale and improve overall health outcomes. Here are some data management practices for healthcare providers.
Automate your workflows
Effective use of technology is essential to effectively manage patient information. Thus, ML-based solutions can grant healthcare leaders the power to embrace the incoming records and use them to their optimal potential. Among the most popular tech tools for the medical sector are:
1.Electronic Health Records – to collect digital health information for patients.
2.Referral trackers – to monitor patient referrals.
3.OCR solutions – to automate paperwork.
4.Remote patient monitoring – to render medical services online, and others.

Source: Unsplash
Use cloud storage to ensure interoperability
The growth of this market is linked with the popularity of wearables, IoT, and Big Data. COVID-19 has also taken a hand in the increasing adoption of cloud computing. But first and foremost, cloud storage helps attain the interoperability of data. The latter refers to the ability of a specific medical system to communicate with other systems without any access and implementation restrictions. Interoperability further translates into easier record management for both providers and patients.
Therefore, cloud adoption leads to improved patient outcomes and better record handling for medical facilities.
Protect Sensitive Data
On the flip side, electronic storage increases the surface for security breaches. Leaks compromise sensitive data and incur monstrous fines for providers. For example, HIPAA violation penalties can amount to $1.5 million annually. Therefore, medical facilities must ensure robust protective measures to keep sensitive information safe.
Safety measures include restricted access to sensitive records and applications as well as encryption and offsite backups. Security audits are also important to discern areas of concern and reinforce protective measures. Medical providers should also maintain IoT devices on their separate networks to prevent leaks and data abuse.
The Final Word
It took quite a time for the medical industry to embrace technology. However, IT infrastructure is a pertinent element for the effective handling of medical data. As the volume of records grows, mastering data management in healthcare is becoming a sought-after practice. Coupled with technology, it can unlock the path to better and personalized healthcare and leave behind operational silos and communication lags.
Streamline your data management with AI
Tired of manual data processing? Want to streamline data management in your healthcare organization? Contact us, and our consultants share their ideas on improving it.