The last decade has been a good one for face recognition technology. Although it has existed since the 1960s, any large-scale attempts to successfully implement it failed. The main reason being that it lacks precision and scalability. Everything changed in the late 2000s.
In 2011, both the Pinellas County Sheriff’s Office and Panama’s Tocumen airport implemented their own facial recognition systems with impressive results. Drug smuggling and organized crime in Panama decreased significantly, and the time it took to process criminal investigation for Pinellas County Sheriff’s Office went down drastically.
Mainstream applications followed next.
Facebook has rolled out their face recognition feature that alerts you when untagged pictures and videos of you are uploaded in 2012. Google has leveraged the company’s substantial experience in AI and machine learning to build Google Photos in 2015. Last year, Apple introduced Face ID on iPhone X.
What is face recognition technology, and why is it the “next big thing” in the tech world?
What is Face Recognition
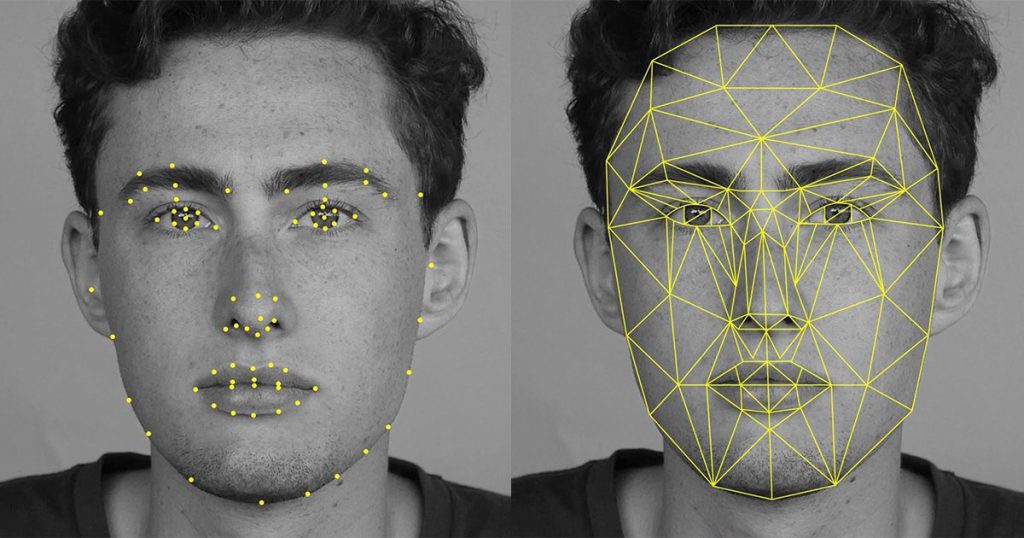
Face recognition technology has one goal: to identify human faces. Out of all biometric systems available, it is the least intrusive and fastest technology.
Instead of asking people to scan their fingerprints, hands or irises, face recognition systems can take pictures of people’s faces unobtrusively. In most cases, the subjects are not even aware of the process. This removes the feeling of being under surveillance or invasion of privacy.
Facial recognition systems are also highly effective in producing results, all thanks to the use of neural network algorithms.
Our brain recognizes different features of a face – the space between the eyes, the height of a hairline, width of a nose – subconsciously. The facial recognition algorithms need to do that intentionally.
Neural networks are modeled on the human brain, and thereby try to mimic the process of recognizing a face. The way neural networks are constructed is best explained by the MIT:
“A neural net consists of thousands or even millions of simple processing nodes that are interconnected. Most of them are organized into layers, and they’re “feed-forward,” meaning that data moves through them in only one direction. An individual node might be connected to several nodes in the layer beneath it, from which it receives data, and several nodes in the layer above it, to which it sends data.
To each of its incoming connections, a node will assign a number known as a “weight.” When the network is active, the node receives a different data item — a different number — over each of its connections and multiplies it by the associated weight. It then adds the resulting products together, yielding a single number.”
How does this translate into a facial recognition system?
Once a face is captured with a 2D or 3D camera, a neural network algorithm analyzes the face to create a unique, digital template. Much like our human brain, the algorithm measures things like the distance between the eyes, the shape of a nose, etc. down to a micrometer in order to “remember” what we look like.
Face recognition technology can also account for variances that can change our appearances. Some examples are facial hair, lighting, and picture angles.
Once the template is created and stored, there are many different possibilities as to what it can be used for: detection, verification or recognition.
Differences between Face Detection, Face Verification, and Face Recognition.
There are several areas where face recognition technology can be applied. The areas are often confused.
Face Detection
Face detection is a broader and simpler term than face recognition. Face detection is concerned with identifying if a human face is present in an image or video, not whom it belongs to.
Face detection has several applications. Camera auto feature uses face detection to determine what parts of the picture are most important. Face detection can also be used to count how many people have entered a particular area. It is also used by self-driving cars to determine if a human is crossing the road.
A trivial use of face detection that you’ve probably experienced yourself is Snapchat’s filters . The filter looks for a presence of a human face and then maps the facial landmarks (eyes, nose, lips, etc) to know where to place, for example, a flower crown or cat ears.
Face Verification
Face verification, also often referred to as face authentication, is about validating an identity based on the image of a face by checking against an existing database.
Face authentication involves comparing an input image only with the image that belongs to the identity the person claims to be. In other words, the system will only compare your face to one picture, not the whole database.
Face Recognition
Face recognition, also called identification involves comparing one input image to all images in an image library in order to determine who the input image belongs to. Or if it does not belong to the database at all.
An example of a face recognition system would be submitting a picture of a suspect to the police database to produce a match, such as they did at Panama’s Tocumen airport.
Real-life Applications of Face Recognition Technology
Face recognition technology is used in many industries, from a way to pass the time to matters of national security.
Health
In the last few years, some hospitals started to use facial recognition systems to make patient processing easier. The system matches the right patient to their records, thereby preventing record duplicates or record oversight.
Another area where facial recognition is used, is emergency situations.
Either on site of an accident or during the transportation to a hospital, patients are often uncommunicative or unresponsive, which makes it hard to obtain medical information vital to the medical care. Facial recognition offers a fast way to access the medical information and, in many cases, speed up the process of providing necessary medical care.
Facial recognition can also help with screening for certain diseases. For example, researchers at Duke University developed an Autism & Beyond app that uses the iPhone’s front camera and facial recognition algorithms to screen children for autism.
Security
The security sector is a veteran when it comes to using facial recognition.
Face verification has been used at many country borders ever since the digitized biometric passport was introduced in 2006.
As we’ve mentioned before, police forces are avid users of face recognition technology as well. One of the most memorable accomplishments of this technology was in 2016 when the “man in the hat”, responsible for the Brussels terror attacks, was identified thanks to FBI facial recognition software.
Many high-security facilities, such as government buildings and nuclear plants, implement facial verification technology to check the identities of employees.
Retail, Marketing, and Advertising
Facial recognition is still in its infancy in retail and marketing, but there are some interesting trails done by big companies.
A way to utilize face recognition technology is by placing cameras in retail outlets. That way it is possible to analyze and improve the customer purchasing process by accessing customer information from their social media profiles and offering customized offers and products.
The American department store Saks Fifth Avenue is already using such a system. Amazon GO stores are reportedly using it as well.
Banking
The banking industry is using facial recognition to both prevent fraud and making online banking safer. HSBC launched a Face ID verification option for their corporate clients in more than 24 countries. The Face ID login is even faster than Touch ID.
Conclusion
Face recognition is an emerging technology that can provide many benefits. Face recognition can save resources and time, and even generate new income streams, for companies that implement it right.
What lies ahead for this technology?
It’s difficult to be certain. Some experts predict that our faces will replace IDs, passports and credit card pin numbers. Given the fact how convenient and cost-effective this technology is, this prediction is not far-fetched.
If this prediction becomes a reality, any company that implemented the technology today might gain a competitive advantage in the future.
Work with InData Labs on Your Computer Vision Project
Have a project in mind but need some help implementing it? Schedule an intro consultation with our computer vision software engineers to explore your idea and find out if we can help.