As technology develops and improves at a comparatively quick pace, it is common to hear a range of new phrases being coined every day. One of them is Big data security analytics – a term often used when addressing challenges associated with protecting and analyzing the data of significant businesses and enterprises.
Big Data refers to technology for handling and analyzing enormous volumes of data that exceed the capacity of standard systems. Three factors set Big data systems apart from conventional ones: the volume of data they collect, the speed at which they gather and send data, and the sorts of data they gather (structured and unstructured).
Now we use the term Big Data analytics when we talk about integrating analytics with Big Data. Big Data analytics refers to the process of analyzing and mining Big Data, which enables the development of operational and business information on an unprecedented scale and degree of detail. The desire to understand and use trend data gathered by organizations is one of the primary drivers of Big data software implementation. This article aims to demonstrate how Big Data is reshaping security analytics via the introduction of new tools and possibilities to leverage massive amounts of structured and unstructured data.
Big data security analytics: why it’s important
Although security analytics have been around for a while, a lot has changed in this field with the advent of Big data. For advanced analytics, security analysts may exploit Big data but also employ machine learning. Big data allows them to utilize ML methods such as anomaly detection to identify minute and discrete network abnormalities. Traditionally, cyber analysts and security analysts have been limited to methodologies such as network vulnerability evaluation and correlation analysis.
 The history of data-driven information security may be traced back to the detection of bank fraud and anomaly-based intrusion detection systems.
The history of data-driven information security may be traced back to the detection of bank fraud and anomaly-based intrusion detection systems.
Big data security analytics integrates Big data techniques with cybersecurity skills to assure data security and decrease the likelihood of data breaches.
Identifying Big data analytics types
Now that you know Big data analytics, let’s look at the five types one may understand and use.
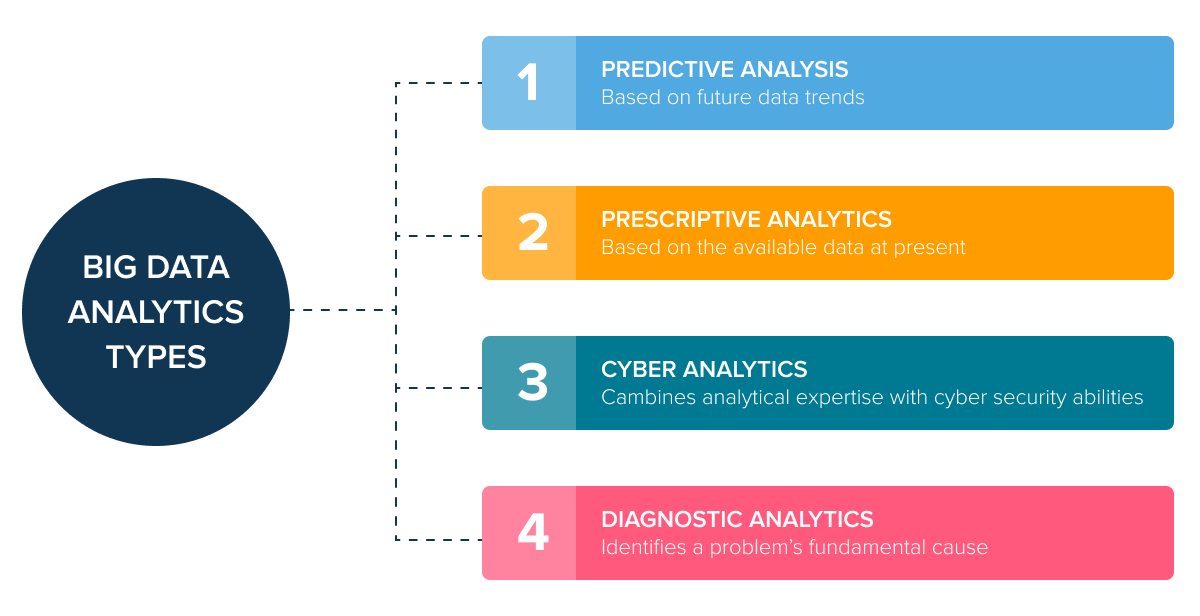
Predictive analysis
Data trends can be predicted with statistics, modeling, data mining, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. It is the most common and user-friendly approach to analytics. This model aims to forecast the outcomes of various company reaction scenarios to a given circumstance.
Source: Unsplash
There are several kinds and sizes of predictive analytics models, but they all utilize a scoring method to determine the chance that a certain result will occur. Transactional profiling, decision analysis & optimization, and predictive modeling are the three pillars of predictive analytics. Predictive analytics explores transactional and historical data for trends to detect risks and opportunities.
Prescriptive analytics
Prescriptive analytics is one of the three primary forms of data analysis used by organizations. Using prescriptive analytics, the analyst may provide the optimal recommendations for a specific circumstance based on the available data. Prescriptive analytics place more emphasis on the present condition than descriptive and predictive analytics, which are more concerned with the past and future.
Cyber analytics
Cyber analytics, which combines analytical expertise with cybersecurity abilities, is a new and rapidly increasing skill set in the BI and data analytics industry. The amount and sophistication of cyber threats have increased with the number of internet-connected devices.
Source: Unsplash
Cyber analysts use a data-driven techniques to detect vulnerabilities and shut attack vectors utilizing powerful software and sophisticated AI security tools.
Diagnostic analytics
Diagnostic Analytics does precisely what its name implies: it identifies a problem’s fundamental cause. It gives a full understanding of a problem’s core cause.
Big data engineers use analytics to find the cause of an occurrence. Diagnostic analytics techniques include drill-down, data mining, data recovery, churn cause analysis, and customer health score analysis. Examining the underlying causes of the most significant churn indicators and identifying patterns among your most loyal clients is advantageous for organizations using diagnostic analytics.
Use cases for Big data security analytics
These are just a handful of the many applications for Big data security. As our dependence on digital information increases, so will the demand for robust Big data security solutions. Let’s discuss the most prevalent uses for Big data security.
Network traffic examination
Large organizations generally see a substantial amount of traffic entering and leaving their networks. Network professionals often overlook anomalies as they strive to keep up with this amount of traffic.
However, Big data security analytics provides quick reporting of abnormalities and severe scenarios. Network traffic behavior may be rapidly monitored by security professionals.
User behavior studies
The involvement of customers with the IT infrastructure is an ongoing activity. However, traditional network monitoring techniques make it impossible for security analysts to keep a careful check on every user’s activities, mostly because it requires a great deal of time when the customer base is vast.
However, Big data security analytics tools enable this and aid security analysts in doing customer-level analysis with little resources. In addition to facilitating the construction of user profiles, this eliminates internal hazards.

Source: Unsplash
Threat evaluation
In the world of cybersecurity, scanning for risks has been a common activity for decades. Before the existence of Big data, it was already in use. Since Big data made threat detection more effective, security analytics has risen tremendously.

Cloud security monitoring
Cloud computing is now one of the most popular topics in the IT industry, and enterprises are adopting cloud infrastructure in large numbers. Big data security analytics is also an excellent cloud monitoring method that requires no human intervention.
Top 3 Big data security analytics tools
The sector employs a variety of Big data analytics vendors in order to ensure security. While some focus on specific use cases, others are broadly applicable in all situations. Here, we will discuss the top Big data technologies to consider.
LogRhythm
LogRhythm is a leading SIEM system that provides comprehensive security analytics. Among its most popular services are User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA), Security Orchestration, Network Detection and Response, and others.
It has worked with a number of major clients throughout the years, including NASA, Gartner, Cargill, etc.
Security analytics from RSA
RSA security is a popular security analytics system that provides security analysts with a range of pre-built reports to help them get started with network analytics immediately. It makes extraordinary use of the network’s data collecting.
In addition, RSA Live is offered to assist with data processing and correlation rules.
IBM QRadar
Last but not least, IBM’s QRadar is a comprehensive cybersecurity system with Big data integration and analytics for cybersecurity. Even while the infrastructure is rather broad and provides a wide variety of services, your setup becomes hard if it is insufficient.
A number of Big data security analytics vendors are being used by the industry in order to provide security. While some concentrate on certain use cases, others are generally suitable for all circumstances. Here, we’ll talk about the top Big data technologies you could consider.
Big data analytics security and privacy challenges
Software security companies face new challenges as Big data quickly grows due to the evolving threat environment, the abundance of sophisticated tools, and the processing power at the hands of cybercriminals.
For effective protection, the correct combination of techniques, human insight, expert knowledge of the threat environment, and quick processing of substantial Big data security analytics is needed. A typical end-user utilizes a variety of mobile and desktop devices to access hundreds of websites daily and a growing number of operating systems and applications.

Source: Unsplash
As a consequence, there is an overwhelming and constant increase in the amount, speed, and variety of information that is produced, shared, and transmitted. We’ll talk about how each point accelerates at a startling rate and causes security firms to change the way they approach threats.
Volume
The threat environment is altering in numerous ways as access to technology continues to advance, including an increase in the sheer volume of threats. Imagine if, in the 1990s, the typical user received one or two spam messages per day, but over 20 years later, over 200 billion spam messages were sent out each day. Similar increases may be seen in both file transfers and online page visits, giving thieves a wide range of targets.
Variety
Hackers use new strategies that are also more extensive with each passing year. Cybercriminals are also becoming better at creating tools in real-time. For instance, modern spyware regularly makes it past quality control checks.

Source: Unsplash
To ensure that it is undetected, fraudsters test it on a range of hardware and operating systems. In truth, malware components are no longer restricted to home computers and may be copied in hundreds of different ways. Additionally vulnerable to multi-platform infection are mobile devices.
Velocity
Security companies have a tremendous pace problem because of the daily need to manage, store and analyze this enormous amount and diversity of data. The instability of the internet over time makes the issue worse. On the Internet, changing IP addresses is easy, rapid, and difficult to notice, unlike changing a physical street address, which requires leaving substantial proof.
As a result, moving from one place to another quickly and conveniently without affecting the environment is possible for both individuals and businesses.
Big data analytics for cybersecurity
Corporate organizations are now more vulnerable to cyberattacks than ever before as a result of the rapid digitization of the business sector. A Big data analysis for business may provide protection against these attacks.
An in-depth analysis of Big data security analytics systems’ current implementation levels, advantages, and difficulties is provided in the “Big Data and Information Security” research by KuppingerCole and BARC.
Threats to cyber security are growing
Due to the growing adoption of cloud and mobile services, the idea of a corporate security perimeter has all but vanished in recent years. As a result, information security has undergone a profound paradigm shift from traditional perimeter protection tools to tools that monitor and identify malicious activities within corporate networks.
Traditional approaches to information security are plainly out of date, as seen by cybercriminals’ more sophisticated attack techniques and the rising importance of malicious insiders in numerous recent large-scale security breaches.

For example, if a large number of users are suddenly trying to access a network from the same IP address, this could be an indication of a denial of service attack. By identifying these patterns, Big data security analytics can help organizations prevent and respond to security threats.
VPNs are often used in conjunction with Big data security analytics. By encrypting data that passes through the VPN, VPNs ensure that only authorized users can access the network. This makes it more difficult for unauthorized users to obtain sensitive information or launch attacks.
Additionally, by encrypting data, VPNs can help protect organizations from spying and other forms of surveillance. As a result, VPNs can provide an additional layer of security for organizations that use Big data security analytics.

Source: Unsplash
Businesses must reconsider their approaches to cybersecurity
Leveraging analytics is essential for maximizing cyber resistance. Organizations must reconsider their cybersecurity principles in light of the fact that assaults are becoming more intelligent and persistent and that every company must defend itself against every kind of attack while an attacker only requires one successful effort. They must transition from pure prevention to the PDR paradigm, which stands for prevent, detect, respond.
What role Big data analytics will play in the future?
Improved detection is the key component of this strategy, and Big data analytics may help. The detection process must be able to recognize shifting use patterns, conduct complicated analyses quickly and almost in real-time, and carry out complex correlations across a range of data sources, including server and application logs, network events, and user activities.
This necessitates using Big data analytics for security intelligence, allowing the analysis of huge quantities of current and historical data. Organizations may increase their cyber resilience by combining security, analytics and AI to fight cyberattacks.
Big data analytics for cybersecurity will only become more important as companies try to protect themselves effectively against rising cybercrime. In fact, the global Big data analytics market is expected to keep expanding and will reach $420.98 billion in value by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 10.9% between 2020 and 2027.
Leverage Big data analytics with InData Labs
Need help with Big data analytics solutions development? Contact us, and we’ll set up a call to discuss your business needs and how we can apply technology to it.