Migrating data to the cloud can become a difficult decision for companies that have spent decades using the physical infrastructure. As a result, some businesses remain hesitant about this transition, despite the salient benefits of data migration. Those who are more decisive stand to score $1 trillion in value as a result of cloud adoption.
If you’re among the doubters, then understanding the core business benefits of cloud adoption and potential pitfalls will help you make the right call.
What is data migration? Main triggers
Data migration generally refers to shifting the existing data to new storage, powered by the cloud service. On a broad level, the ascent of data center migration to the cloud is accelerated by the following global trends:
- The growing amount of Big data – by 2025, the global datasphere will grow to 175 zettabytes.
- IoT system integration – the number of Internet of Things devices is expected to amount to over 29 billion by 2030.
- Remote collaboration and hybrid work setting – 74% of U.S. companies are using or plan to implement a permanent hybrid work model.
- The innovation imperative – ingenious technologies require a more flexible and low-cost data architecture.
The combination of these drivers stands behind the rapid adoption of cloud environments in business settings. By 2023, the global cloud computing market is expected to garner over $1,554 billion.
Along with purely technical reasons, there’s something else that urges companies to a more flexible data environment. The potential benefits of migrating data to the cloud hold the promise of added business value and help carve a digital transformation path – easier and in a cost-effective way.
10 advantages of data migration to know
Weighing the pros and cons of migration allows you to craft the best strategy to achieve a smooth transition to the cloud.
Let’s see the main benefits of data center migration to the cloud that make a difference for the majority of adopters.
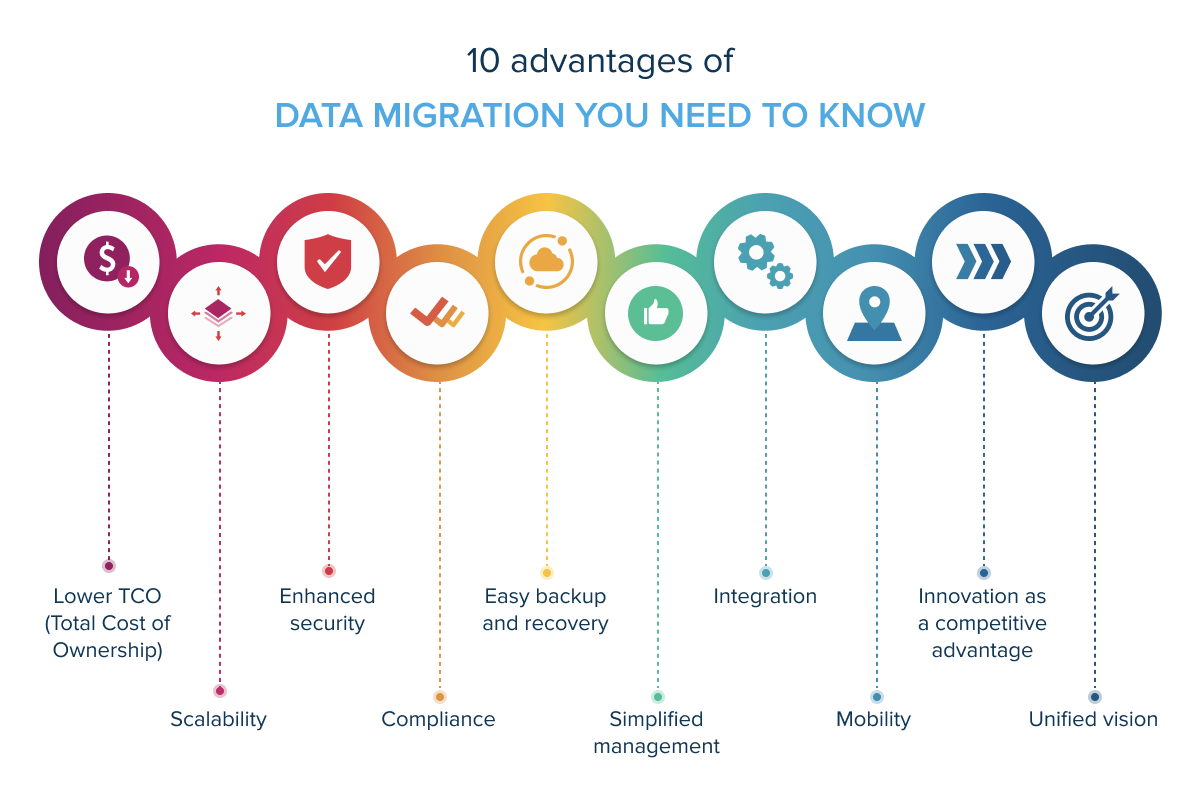
Lower TCO (total cost of ownership)
The cost-saving potential of data migration to the cloud is one of the main levers behind most digital journeys. Although cloud services can initially be more expensive than running on-premises architectures, they pay off over time if you learn how to operate them efficiently.
According to Gartner, Infrastructure-as-a-Service software turns out to be 55% less expensive compared to on-premise centers over time.
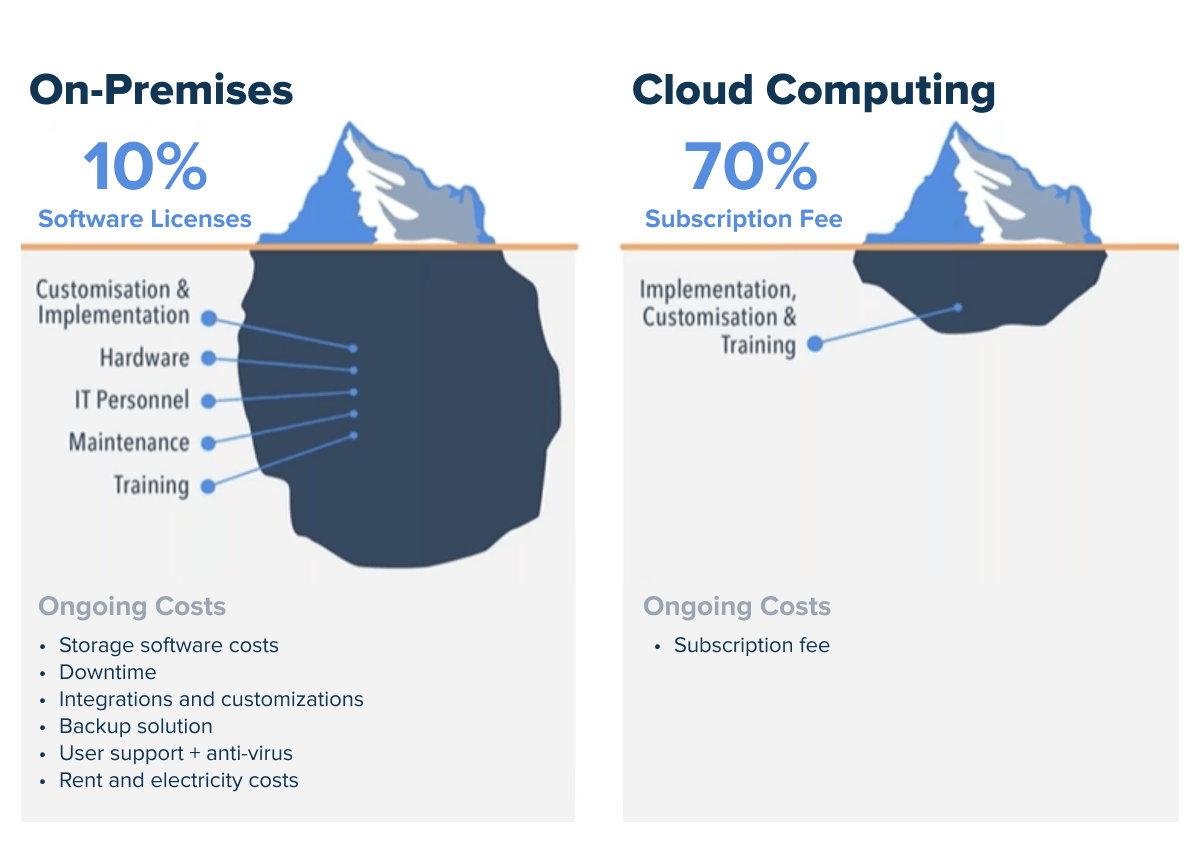
Lower TCO mainly stems from less resources being spent on maintenance, the absence of Capital costs, and the ability to optimize workloads to make them less costly. It also includes indirect value such as time-to-market improvements and flexibility to reach more markets.
The key to cost efficiency is to choose the right cloud model and storage type as well as right-size the services to fit your workloads. But most importantly, you need to calculate the TCO at the onset of your journey to capture the value of savings. You can determine the cost by either using TCO calculators or turning to data migration consultants.
Scalability
On-demand scalability is among other incentives for the cloud makeover. With physical IT infrastructure, it can take weeks or months to scale up operations after they’ve reached capacity. In contrast, with cloud computing, you can ramp up your resources instantly on-demand — without having to purchase additional hardware or software licenses first.
This provides greater freedom for both small businesses with limited budgets and large enterprises with complex needs that require a high degree of customization or scalability to meet changing business demands over time.

Source: Unsplash
Enhanced security
According to Oracle, 66% of C-suite executives consider security to be among the top advantages of data migration to the cloud. There are many reasons why cloud security is seen as more effective than traditional security measures.
First, most cloud providers offer a-la-carte security features and dedicated security tools for infrastructure owners. Second, providers have more resources to invest in security than most businesses do – thanks to the shared cost model.
Another reason is that cloud providers take over consistent patching and security management. In most cases, security patches are done automatically by the provider.
Compliance
On-premise environments are deemed to be inherently more compliant. However, the cloud allows you to adjust its policies to meet the regulatory compliance and security requirements of your business.
Also, distributed cloud systems cover the majority of data protection regulations, including GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and others. For example, AWS regularly receives third-party validation for thousands of international compliance requirements.

Source: Unsplash
It means that you can offload a large share of your compliance worries to a provider and get the luxury of ongoing compliance management with fewer costs and effort. Keep in mind that all compliance assurances are listed in the service-level agreement, so make sure to check the necessary provisions beforehand.
Easy backup and recovery
Traditional environments presuppose tape-based backups that are both time-consuming and tedious. Conversely, data warehouse migration to the cloud introduces you to one-click backup and recovery capabilities. With virtualization, you can backup an entire server and store those backups offsite.

Simplified management
Cloud migration takes the hassle out of maintaining, updating, and protecting the infrastructure. The latter includes the hardware, software, networking, and facilities that run on virtual servers.
Also, you can even monitor both your physical storage and cloud data warehouse within a single interface if the cloud provider offers a central management tool.
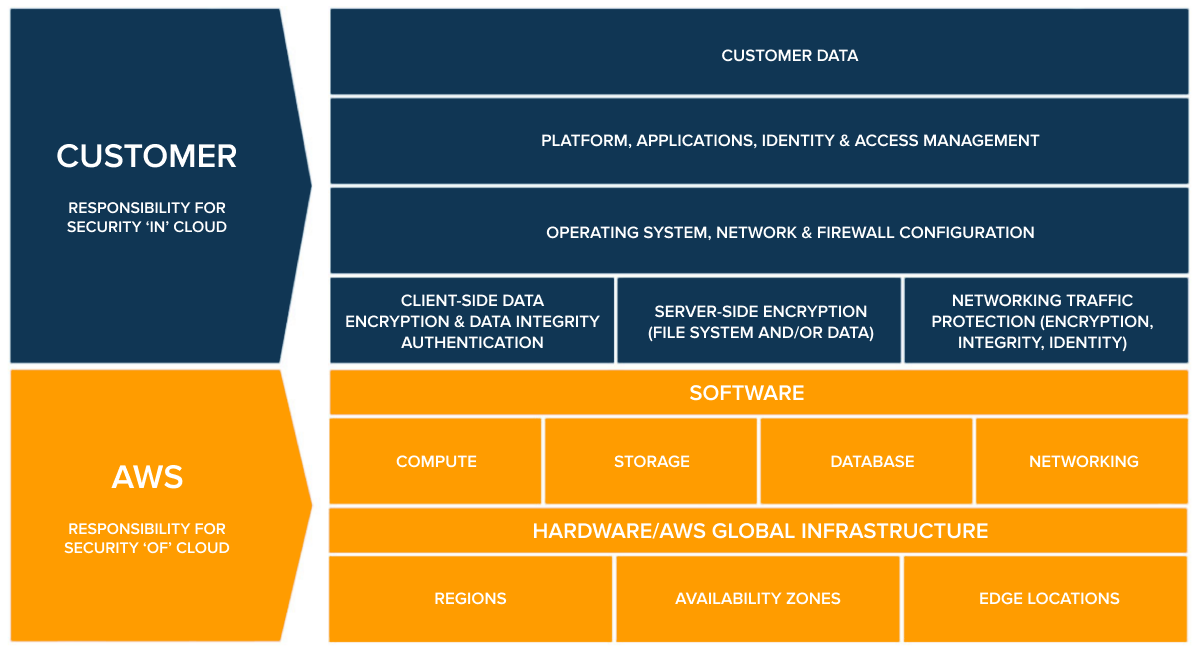
Source: AWS Shared Responsibility Model
Integration
By migrating data to the cloud, you tap into rich, built-in integration capabilities that ensure data interoperability within your company. This enables organizations to use a variety of cloud-based services together and create a more comprehensive and integrated solution.
Cloud integration can also help you improve visibility into your business and produce more accurate reports. For example, the Azure ecosystem allows you to connect business apps, systems, and data into a unified infrastructure through 600+ out-of-the-box connectors.
Mobility
The cloud has been a game-changer for businesses when it comes to mobility. Data center migration to the cloud enables businesses to access their data and applications from anywhere in the world. It makes the employer more flexible, collaborative, and productive – both in and out of the workplace.
The demand for more portable digital estates is accelerated due to the rise of ‘Bring Your Own Device’ (BYOD) policies. Thus, a massive 82% of companies are now implementing BYOD to at least some extent.

Source: Unsplash
Innovation as a competitive advantage
With the cloud, businesses have access to a whole range of new technologies that can help them be more innovative. From Big data development to virtual reality to AI customer service, the transition opens up new lucrative possibilities for businesses to explore. And better yet, you can innovate with far more capital efficiency.
The innovation potential is complimented by a decreased time-to-market that the transition grants you. According to McKinsey, 75% of the cloud’s predicted value comes from boosting innovation.
Unified vision
By migrating your data warehouse to the cloud, you establish a unified architecture, which is essential for businesses that want to make data-driven decisions. An integrated view gives businesses a single vision of their data, which makes it easier to understand, visualize, and act upon. Moreover, businesses can avoid the need to maintain multiple silos.
Common challenges of cloud data migration
According to McKinsey, 75% of companies leak their share of cloud value as they are haunted by budget overruns. And even if the transition falls within the budget scope, the other 38% of organizations struggle to complete the shift on time. Let’s see what causes these failures.
Cost management
While migration of your data center to the cloud can improve ROI in both the short- and long-term, you still need significant upfront investment to make it happen. The associated expenses may include everything from data collection to provider fees to talent compensation. Failing to properly analyze the potential financial impact whittles down the profitability of your project.
Solution: To avoid this pitfall, you need to run a comprehensive infrastructure audit, identify your business case, and move incrementally through batch adoption. In this case, you can accurately estimate your data science projects and break them down into more manageable pieces.

Source: Unsplash
Security and compliance
When moving data to the cloud, the security of assets both in transit and at rest is critical. Large volumes of input in motion are highly vulnerable to threats, while wrong access misconfigurations leave the information exposed in the infrastructure. Also, as providers operate on a shared responsibility model, you have to take over securing data and workloads.
Solution: The right choice of a cloud provider and a service as well as having the right safeguards in place will keep your assets protected and compliant with the regulations.
Vendor lock-in
As organizations shift to virtual ecosystems, they need to be aware of the risks of vendor lock-in. Vendor lock-in occurs when an organization becomes reliant on a particular vendor and gets stuck in an inefficient cloud. This can lead to higher costs and reduced flexibility if the organization decides to switch vendors.
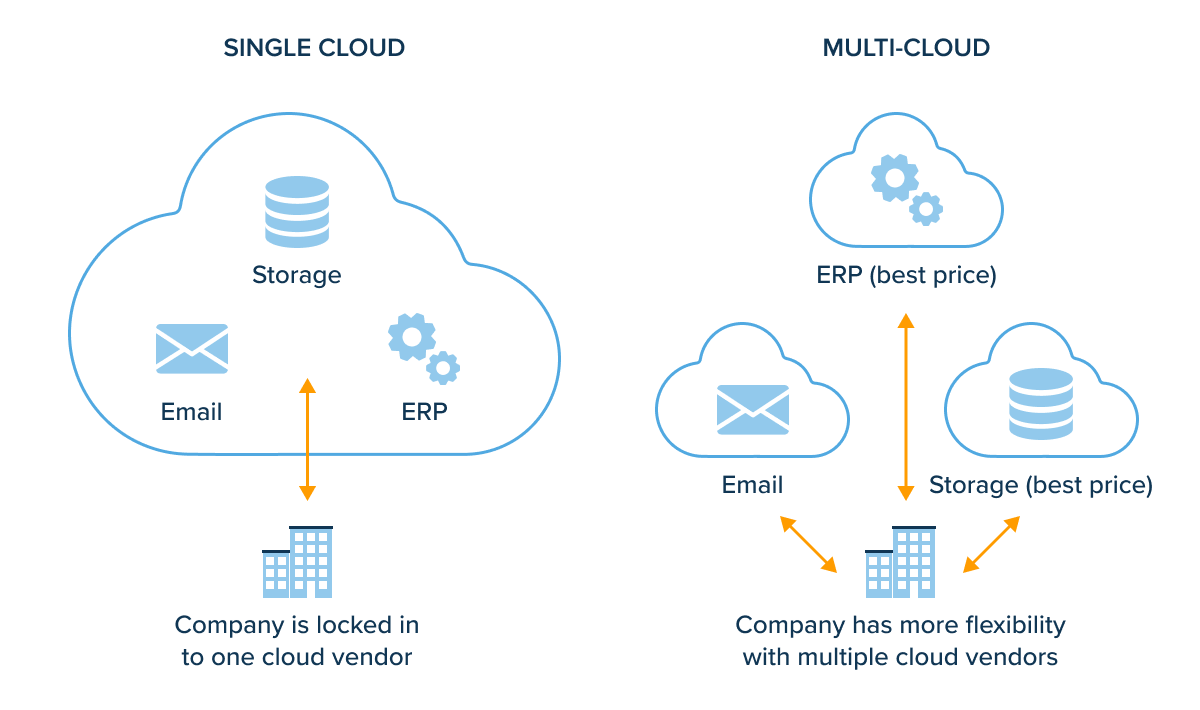
Solution: To avoid vendor lock-in, organizations should carefully consider their strategy, choose a vendor that will best meet their needs, and create an exit strategy. You can also consider using multiple vendors to reduce the risk of vendor lock-in.
Adoption resistance
People are the core element of your technological excellence that ensures you make the most out of your cloud investment. Employee inertia can stem from the absence of leadership buy-in, a vague business case, and unawareness of the value this transition brings.
Solution: To make your business units more receptive, make sure that you provide proper training and support to employees, anchor your business case to end-user needs, and promote a cultural shift to embrace the change.
Data migration to the cloud strategy: 3 pillars
All the challenges we mentioned above have one commonality – they all are the result of poor data migration to the cloud strategy. True cloud adoption and modernization cannot work at full capacity unless the technology, people, and processes grow in lockstep.
Technology
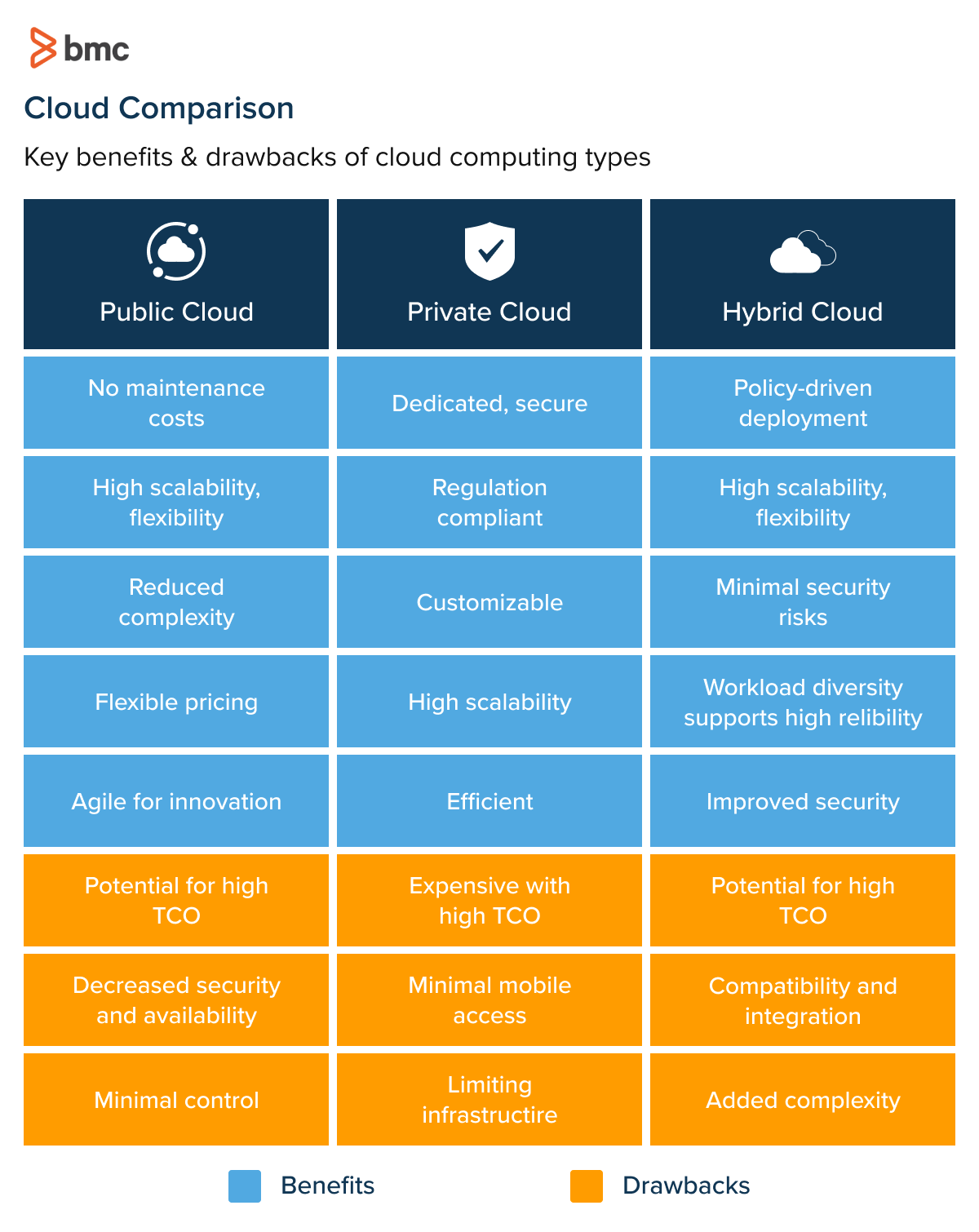
First of all, you need to decide on the optimal cloud environment that syncs with your business needs. There are three types of cloud infrastructures.

Source: Unsplash
Single public
Single public clouds are operated by a single service provider and are accessible to anyone who subscribes to the service. Public clouds are generally less expensive than private clouds, but they are also less secure and offer less control to the subscriber. This infrastructure type alleviates the burden of server operation and maintenance, thus reducing the total cost of ownership (TCO).
This set-up supports businesses that want to modernize legacy architectures at less cost while focusing on essential business functions.

Source: Unsplash
Single private
Single private clouds are operated by a single organization and are not accessible to the public. Private clouds can be hosted on-premises or off-premises. This infrastructure is more expensive but offers more security and control. A single private set-up is a common approach for organizations concerned about data security and compliance.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid environment thrives on a combination of on-premises and public services with communication between the two platforms. A hybrid infrastructure allows data and applications to remain on-premises while making the most of the scalability, security, and pay-as-you-go pricing made possible by public cloud platforms.
An organization may choose to keep sensitive data on-premises while leveraging the public cloud for less sensitive data or to accommodate occasional spikes in network traffic.
People
According to AWS, a Cloud Enablement Engine framework requires a cross-functional ambassador team that is skilled enough to implement the governance, best practices, training, and architecture needed for the transition.
At the onset of your transition, you will need to secure the following specialists:
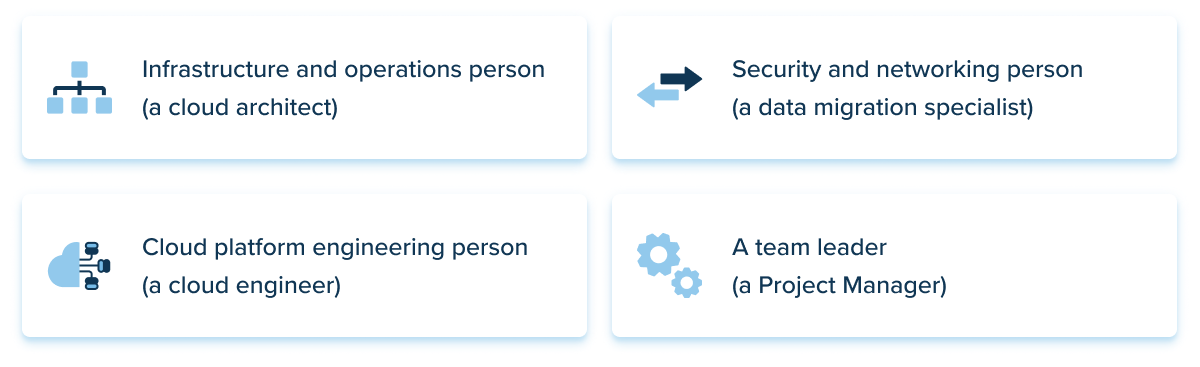
Failing to fill these roles will counteract your effort and limit the necessary competencies to successfully perform a transition. Also, the people component applies to your in-house team which will need guides and training sessions to navigate the new architecture.
Processes
Lastly, you should define and implement processes that will establish how the organization will deliver on its cloud strategy. Thus, by having a solid change management plan in place, you can minimize the impact of this disruption and ensure a smooth transition to the cloud. Change management can also improve collaboration within an organization.
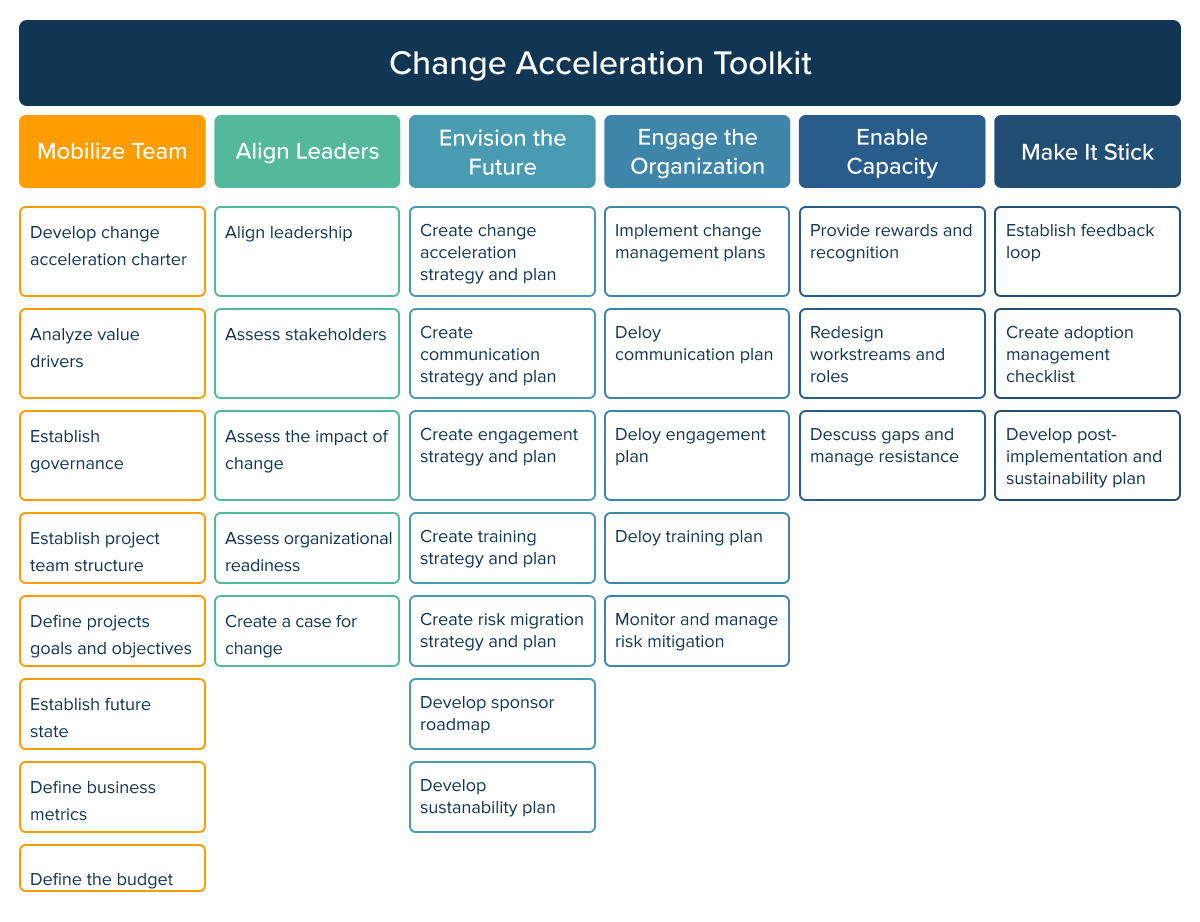
By aligning your processes, team, and technologies, you will set the course for the long-term value provided by the data warehouse migration to the cloud.
How to migrate data to the cloud in four steps
The exact workflow of your data center to cloud migration depends on the migration approach. However, there are four universal milestones that apply to all types of transitions. Building on the experience of InData Labs, here is a data center migration to the cloud checklist.
Prepare
First, you need to prepare input for your Big data migration to the cloud. At this stage, you pinpoint the interdependencies between your applications and databases.
All your workloads should also be divided into categories by migration type. The database workloads may include everything from simple, homogeneous input to complex, heterogeneous one.
At this stage, you should also pay due diligence to your information through auditing and profiling. This process will help you avert costly errors such as duplication, erroneous input, and others.
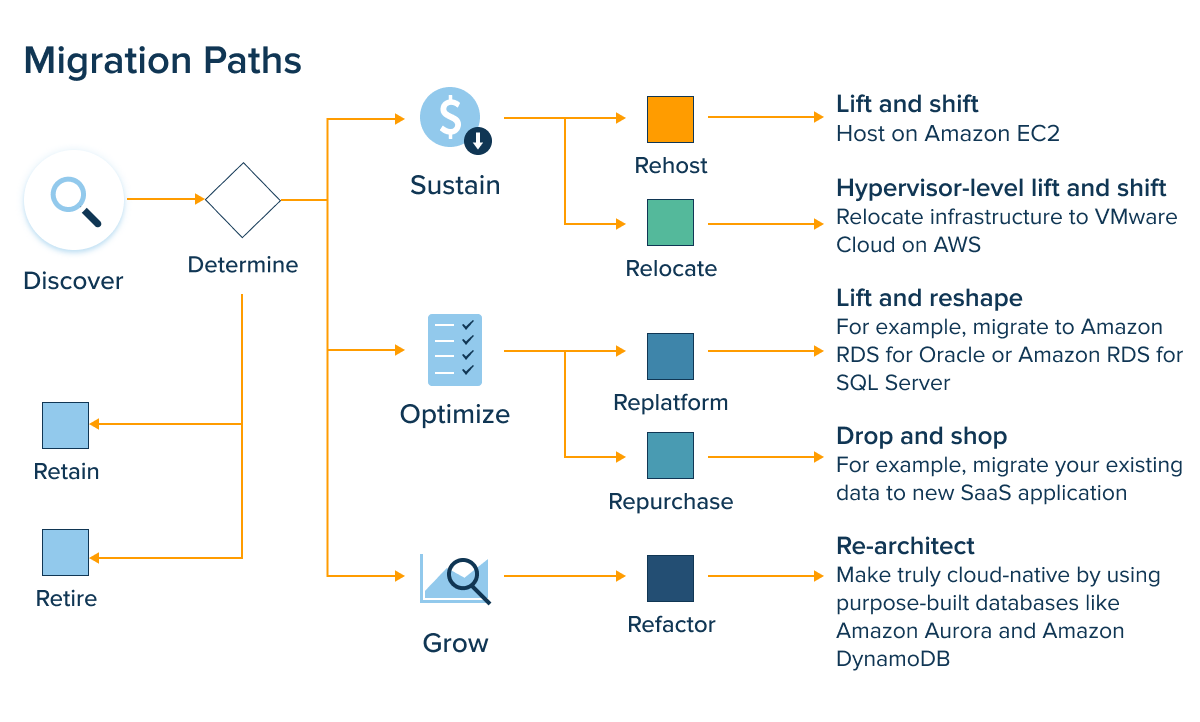
Plan
Next, you should decide on the type of your transition. The main transition categories include rehost, replatform, relocate, repurchase, refactor, retire, and retain. These range by the amount of effort you should put into the new architecture where rehost is the most simple.
The exact path depends on your unique business requirements, deadline, budget, and resource allocation. Thus, if your application is not outdated and has a long shelf life, you can perform a rehost instead of revamping it.
Migration can be a daunting task, especially when important data is at stake. But by taking the time to backup your data before migrating, you can avoid any potential disasters.
Data backup is also an important part of any migration process, as it gives you a safety net in case anything goes wrong. Thus, you can rest assured knowing that you can always revert to a previous version if needed.
Migrate
Once you’ve specified your strategy, the actual migration takes place. This process follows an iterative approach where conversion, migration, and testing are performed as a cycle of repeated steps. Although there are several techniques designed to facilitate the process, Extract, Transform, and Load is the most popular one.
It combines input from several sources into a consistent data warehouse or another target system. At this point, you might want to get a dedicated ETL engineer, especially if your project is about large data volumes. The new environment is available once the functional and performance testing is completed. Enhanced user experience and reduced risk rate are among the sizable benefits of data migration testing.

Source: Unsplash
Optimize
Optimization and customization will help you make the most out of your cloud investment. To maximize the benefits, you can optimize your bandwidth costs, right-size the services, or perform any other adjustment to address cost, performance, security, or resiliency concerns.
One way to optimize your costs is to use reserved instances. Reserved instances are an upfront commitment to pay for a certain amount of usage over a period of time. In exchange for this upfront commitment, you receive a discount on the hourly rate. This can be a significant saving for companies that use a lot of cloud services.
Upgrading to the cloud for better results
Cloud adoption is moving up the boardroom agenda as organizations acknowledge its vital importance in sustaining growth. From lower processing costs to added flexibility to faster innovation, cloud-first business architectures stimulate revenue uplift and ride the way of the market competition.
But as companies scramble to roll out the new environment, they face a great number of pressures that stem from the cloud immaturity. Migration failures, compliance issues, the lack of resources and other pitfalls set back your share of value. Getting professional help from cloud experts will get your migration off to a good start and save resources and time spent on the transition.
Migrate to the Cloud with InData Labs
Pass on the task of data migration to the Cloud to experts. Contact to schedule a meeting.



