Welcome to Industry 4.0, aka the Fourth Industrial Revolution or 4IR. Now is the latest phase in the digital makeover of manufacturing. This time around, it’s all about big changes driven by analytics, automation, and human-machine interaction.
The impetus for the first Industrial Revolution. The second was characterized by electricity dominance. And the third hinged on initial automation and mechanical innovations. Now, the Fourth Industrial Revolution is being shaped by cyberphysical systems—intelligent computational capabilities. And one of the key types of disruptive technologies behind reshaping the value chain is Artificial intelligence (AI).
In this article, we’ll explore how AI is used in manufacturing. We shall further analyze the most promising AI use cases in manufacturing by 11 leading global manufacturers.
What are examples of AI use cases in manufacturing?
The potential of AI and machine learning algorithms in manufacturing is only beginning to unfold. Beyond their established roles in robotics and automation, AI in manufacturing is now making its mark in broader areas.
Although covering all the AI use cases in manufacturing would go beyond the scope of this blog, let’s delve into the five most impactful ones. These serve as excellent starting points for manufacturers to direct their efforts.
Supply chain management
By harnessing the power of AI and ML in manufacturing, companies are transforming their supply chain strategies, for enhanced efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness.
AI in the supply chain involves predictive analytics, intelligent inventory management, refined demand forecasting, and optimized logistics. AI analyzes factors such as transportation costs, production capacity, and lead times to optimize the supply chain. This results in a streamlined order fulfillment system that guarantees timely deliveries, reduced transportation expenses and heightened customer satisfaction.
Predictive maintenance
This use case of AI in manufacturing empowers companies to observe equipment breakdowns proactively. It helps them minimize downtime and optimize maintenance schedules.
A pivotal component of predictive maintenance is the digital twin—an online replica of a physical asset. It captures real-time data and mimics its actions in a virtual setting.
By merging this digital twin with sensor data from actual machinery, AI in manufacturing can:
- Study patterns
- Spot anomalies
- Anticipate potential malfunctions
The power of automotive AI-based predictive maintenance can be seen in the example of a leading automotive manufacturer- Ford.
Here, distinct digital twins are created for each vehicle model. Each oversees a different production stage—from conception to assembly to operation. Notably, it can precisely pinpoint energy wastage. It also suggests energy-saving opportunities, boosting overall production line performance.
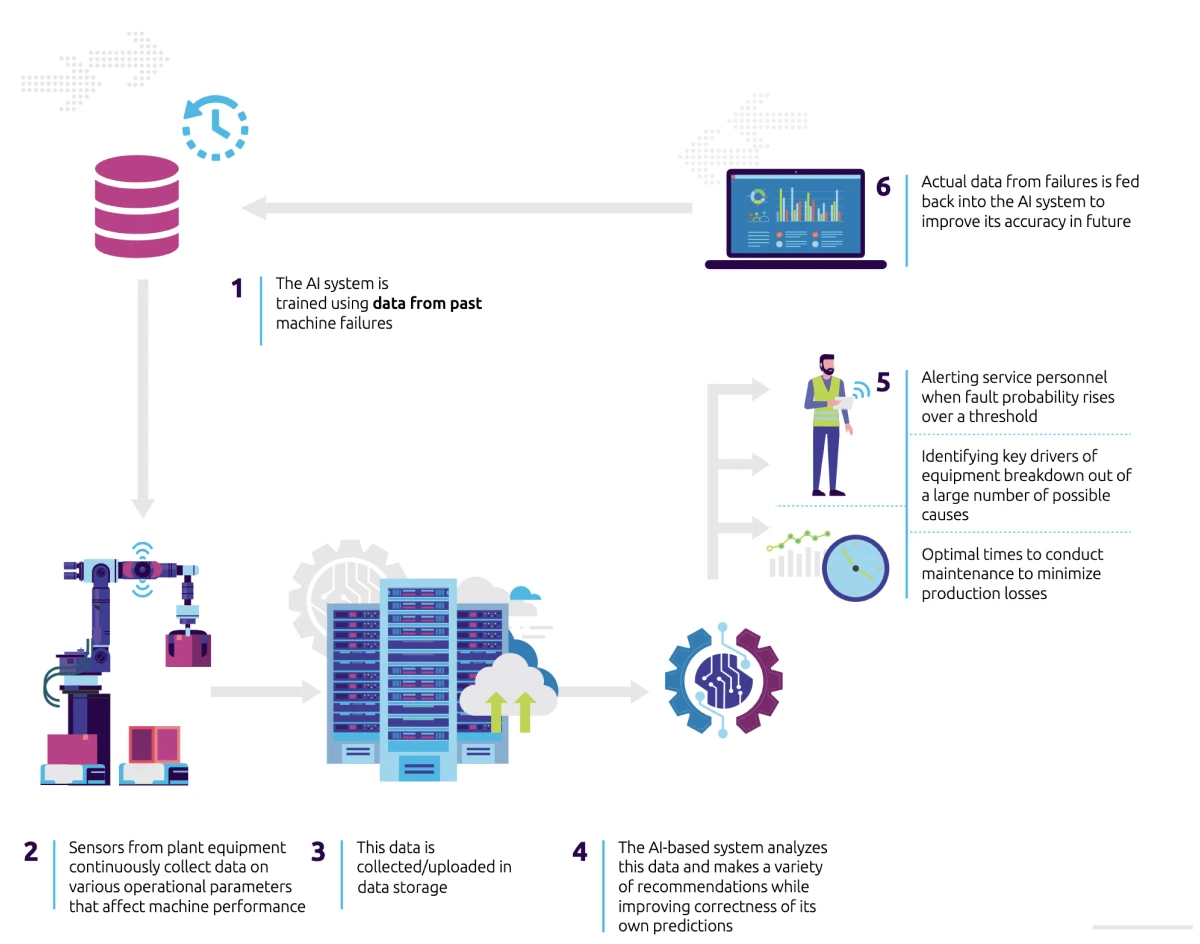
Source: Capgemini
Product quality inspection
Just as recognizing subtle trends can help predict equipment glitches, looking into process details can proactively prevent quality concerns. AI streamlines defect detection by employing intelligent vision systems and video analytics technology. This adept vision system identifies misaligned, missing, or incorrect components with minimal room for human error.
The wide availability of computer vision-based cameras, and advanced image recognition, has made real-time checks during production much more affordable. This application gives manufacturers with a practical way to handle strict industry regulations, especially in fields like automobiles and consumer goods. It proves valuable in following product standards and compliance, which is essential to avoid problems like fines, legal actions, and unhappy customers.
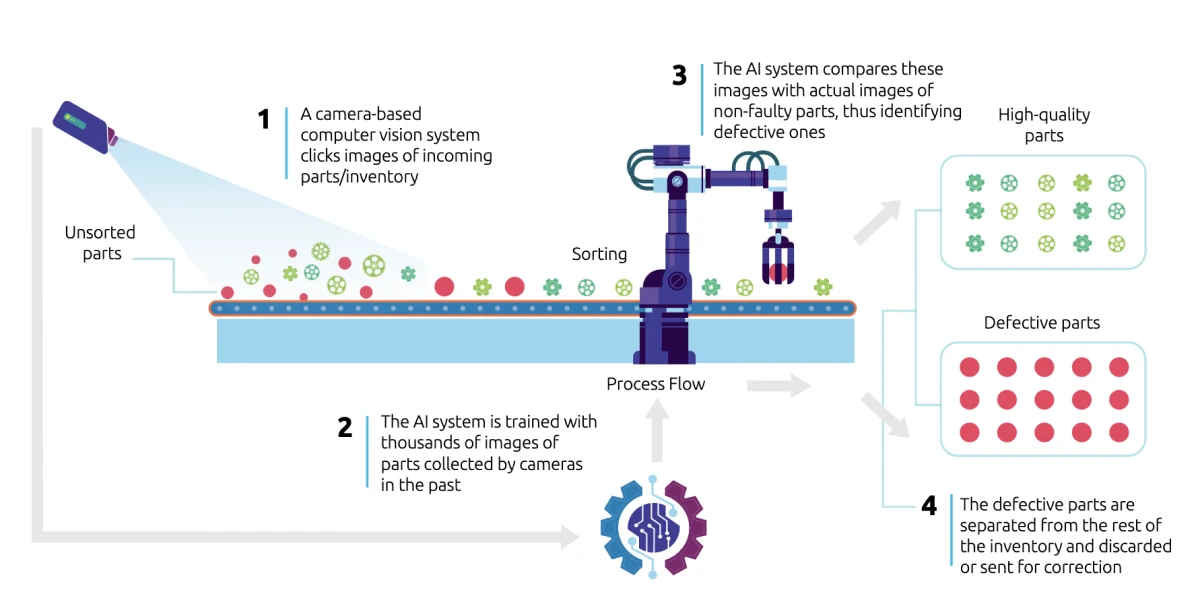
Source: Capgemini
Demand forecasting
Enterprises are partnering with AI companies to leverage ML and anticipate shifts in consumer demand with utmost accuracy. This equips them to anticipate changes in demand and align their production strategies accordingly. Thereby mitigating the risks of running out of stock or holding excess inventory.
Case in point—L’Oréal. The global beauty products leader leverages diverse data sources such as social media insights, Point-of-Sale data, and weather patterns to forecast shifts in customer preferences, predict trends, and optimize sales strategies.
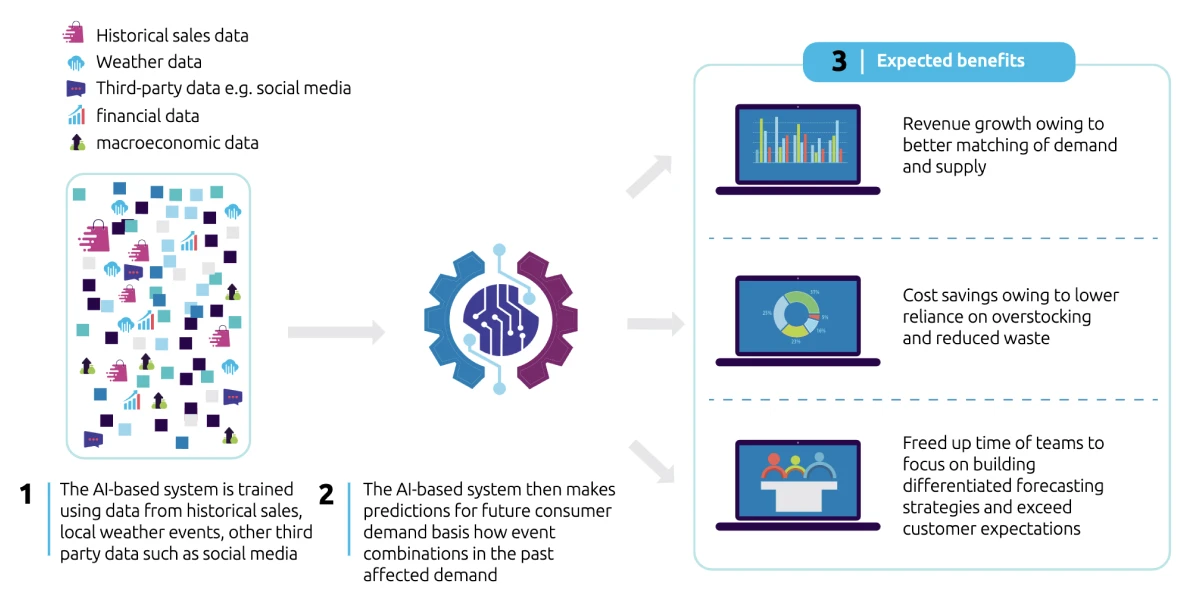
Source: Capgemini
Product innovation
With the integration of AI in manufacturing, companies are embracing more efficient workflows and redefining product development. AI’s standout advantage is its remarkable capacity to swiftly analyze vast data from market trends, customer preferences, and competitive landscapes. This informed approach aids decision-making and crafting products that precisely resonate with market demands.
AI technology captures and monitors design data, empowering engineers to create inventive product designs, shorten testing periods, and gain deeper insights into customer preferences.
Generative AI design software is another impactful AI application. Engineers input parameters and goals, and AI generates multiple design options, expediting design iterations for innovative products.
This results in data-driven decision-making, faster design cycles, and the ability to create products that fit market needs.
How the top 11 companies harness AI for manufacturing excellence
BMW
BMW Group uses AI across its operations, from production to customer experience. It is further embracing AI for manufacturing, enhancing efficiency in its Spartanburg plant. The South Carolina plant produces over 1,500 vehicles daily.
Robots with AI manage the intricate task of welding hundreds of metal studs onto SUV frames, ensuring precision down to the last detail. Even better, if any mistake happens, AI steps in to rectify it. This has saved over $1 million annually.
The technology doesn’t stop on the floor – AI aids inspections, too. Cameras identify issues, making the process faster and smarter.
General Motors
GM is making smart use of industrial AI in its manufacturing processes. They’re tapping into the images captured by cameras on assembly robots to detect potential problems with the robots themselves. The proactive approach prevented unplanned outages.
Working alongside their supplier, this system analyzes the images to identify signs of failing robotic components. A successful test run saw it catch 72 instances of component failure across 7,000 robots.
And here’s why it’s a big deal: just one minute of the assembly line stops can cost GM around $20,000. GM is also embracing AI-based generative design technology to design the next-gen of lighter vehicles. This innovation holds the key to crafting efficient, lighter alternatives for greener vehicles with zero emissions.
By tapping into it, GM engineers can swiftly explore numerous high-performance design choices ready for production. Since 2016, GM has rolled out 14 new vehicle models, slashing an impressive 350 pounds per vehicle. Based on recent reports, GM is working to integrate ChatGPT and incorporate a vehicle assistant that uses AI models behind ChatGPT, tailored for drivers.
Nissan
Nissan Motor Corporation’s ‘Intelligent Factory’ leverages AI, IoT, and robotics to produce next-gen vehicles, while maintaining a zero-emission production system. It streamlines operations like the simultaneous underfloor mounting process. The process previously required six manual steps for components like the battery, motor, and rear suspension. Now, it is executed seamlessly in a single step, thanks to robotic assistance.
From fastening and alignment of suspension links to headliner installation, cockpit module integration, motor winding, and paint inspection. The entire production process will be automated in this intelligent factory.
The production line also incorporates AI-based quality assurance, remote equipment diagnosis, and maintenance solutions. Nissan has also created AI design tools to predict the aerodynamic performance of the new designs. By learning from vast data, AI has significantly reduced simulation durations from days to seconds.
Danone
Danone, the multinational food products leader, is tapping into the power of machine learning to revolutionize its manufacturing processes. It uses ML to predict shifts in demand variability and enhance planning. By harnessing this new capability, Danone has witnessed remarkable improvements in its forecasting procedures, leading to seamless coordination between departments like marketing and sales. And it’s working: their predictions are now 20% more accurate, and they’re losing 30% fewer sales. This change has improved everything, from marketing, sales, account management, and supply chain to finance.
This upgrade has translated into enhanced efficiency and optimized inventory management, particularly for the supply chain. It has led to a 30% reduction in product obsolescence, a 50% decrease in the workload of demand planners, and a 30% reduction in lost sales.
Airbus
Airbus relies on AI across its operations, including manufacturing, quality checks, and the supply chain. Airbus demonstrates a high level of expertise in asset maintenance, in the manufacturing domain. It helps them monitor critical data from machine sensors, like temperature and pressure, sourced from parameters directly influencing machine performance.
The predictive software serves as an early-warning mechanism, enabling Airbus to swiftly halt machines, thereby preventing time and financial resource wastage. They have embraced ML to monitor supplier lead times. Through this, the company has effectively established buffers to guarantee the availability of parts, consequently streamlining assembly lead times. Airbus has also demonstrated manufacturing AI use cases to boost quality. AI-powered defect detection processes empower the company to identify issues early, effectively mitigating potential disruptions in aircraft production. And the outcomes are impressive – they’ve cut lead times by 20% and reduced missing parts by four units.
Intel
As one of the leading silicon manufacturers, Intel has honed its high-value AI strategy in its semiconductor manufacturing. They prioritize AI use cases in manufacturing that offer clear business benefits, practical feasibility, and swift value realization.
Over the past two decades, Intel has successfully implemented various manufacturing AI solutions, deploying thousands of AI models at scale. Their AI solutions cover various analytical stages, from in-line defect detection to advanced process control. Intel’s scaled manufacturing AI solutions have not only delivered substantial financial gains but also sped up manufacturing processes, leading to increased yields and productivity.
Bridgestone Corp.
Bridgestone’s AI in manufacturing case study showcases how AI can reshape manufacturing by fostering meticulous quality control and boosting performance standards. It has launched a groundbreaking tire-building and molding system, called “Examation”. It leverages AI in manufacturing to enhance tire quality, productivity, and consistency.
This AI-driven tool steers the production process in real-time, ensuring every component is assembled under optimal conditions. Additionally, it seamlessly integrates data generated during the tire-building process into the overall factory operations, pivotal in elevating the plant’s process capabilities. The outcome is high-precision manufacturing, with a remarkable 15% enhancement in uniformity compared to traditional methods.
PepsiCo
ML is revolutionizing operations at Frito-Lay, the subsidiary of PepsiCo. They’re using lasers to hit chips and analyzing their sounds to determine texture—automating chip quality checks. Building on this, the company identified more AI use cases in manufacturing within the factory.
When paired with a vision system, a machine learning model predicts potato weights as they’re processed. This move saved the company a significant amount by eliminating the need for expensive weighing elements. Another ongoing project aims to assess the “percent peel” of a potato post-peeling. This data helps optimize the peeling system, potentially saving over $1 million annually for the company in the United States alone.
Kellog’s
Kellogg’s has fully embraced the potential of AI across operations, from enhancing supply chain efficiency to crafting optimal flavor combinations for new products.
On the supply chain front, Kellogg’s leverages AI to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery of materials and products. The technology continually examines various data sources related to demand signals. When disruptions are detected or patterns that could lead to them, the system suggests strategies to avert these challenges.
Kellogg’s AI endeavors are firmly rooted in practicality, focusing on real business challenges and marketplace needs. This ensures a direct impact on business performance and resource optimization. The outcomes speak for themselves – Kellogg’s AI integration has led to reduced waste in the supply chain and a noticeable boost in sales.
Flex
Flex, a global electronics manufacturer, creates printed circuit boards (PCBs) that are pivotal in electronic devices. These need careful checking for quality, but traditional human inspection faced challenges as demand grew faster.
To counter this, Flex adopted an AI/ML-powered defect detection system. This innovation employs deep neural networks to spot defects that escape conventional vision systems and human scrutiny. This technology overhaul streamlined inspections, boosting efficiency by over 30% and elevating product yield by an impressive 97%. This shift also optimally utilized factory floor space by retiring legacy inspection setups, paving the way for other lines and solutions.
Kraft Heinz
Kraft Heinz, a major global food company, has embraced AI for manufacturing to make its manufacturing more efficient and enhance its product development processes. By utilizing AI-powered tools, it identifies waste and inefficiencies in manufacturing and supply chains, leading to optimization. The technology analyzes various factors to optimize processes, swiftly evaluating production and operational aspects that highlight areas for improvement.
For instance, they use AI to optimize the replenishment of tomato paste, taking into account supplier performance scores and predictive analytics. This data helps them receive higher-quality goods, which reduces the need for costly fillers to maintain product quality. Another AI use case in manufacturing involves condition-based maintenance. Sensors on production lines detect vibrations and send data to an external analyzer. This helps predict potential failures, allowing maintenance to be planned during regular windows instead of risking expensive unplanned downtime.
Conclusion
In the era of Industry 4.0, AI use cases are reshaping manufacturing. These 11 AI manufacturing case studies showcase how AI enhances efficiency, boosts quality, and revolutionizes processes. From predictive maintenance to supply chain optimization, AI’s impact drives the industry toward a smarter, more innovative future.
Author bio
Carl Torrence is a Content Marketer. His core expertise lies in developing data-driven content for brands, SaaS businesses, and agencies. In his free time, he enjoys binge-watching time-travel movies and listening to Linkin Park and Coldplay albums.
Forecast goods demand, anticipate sales and seasonality
Predict trends and plan your business steps with custom AI manufacturing solutions.



