
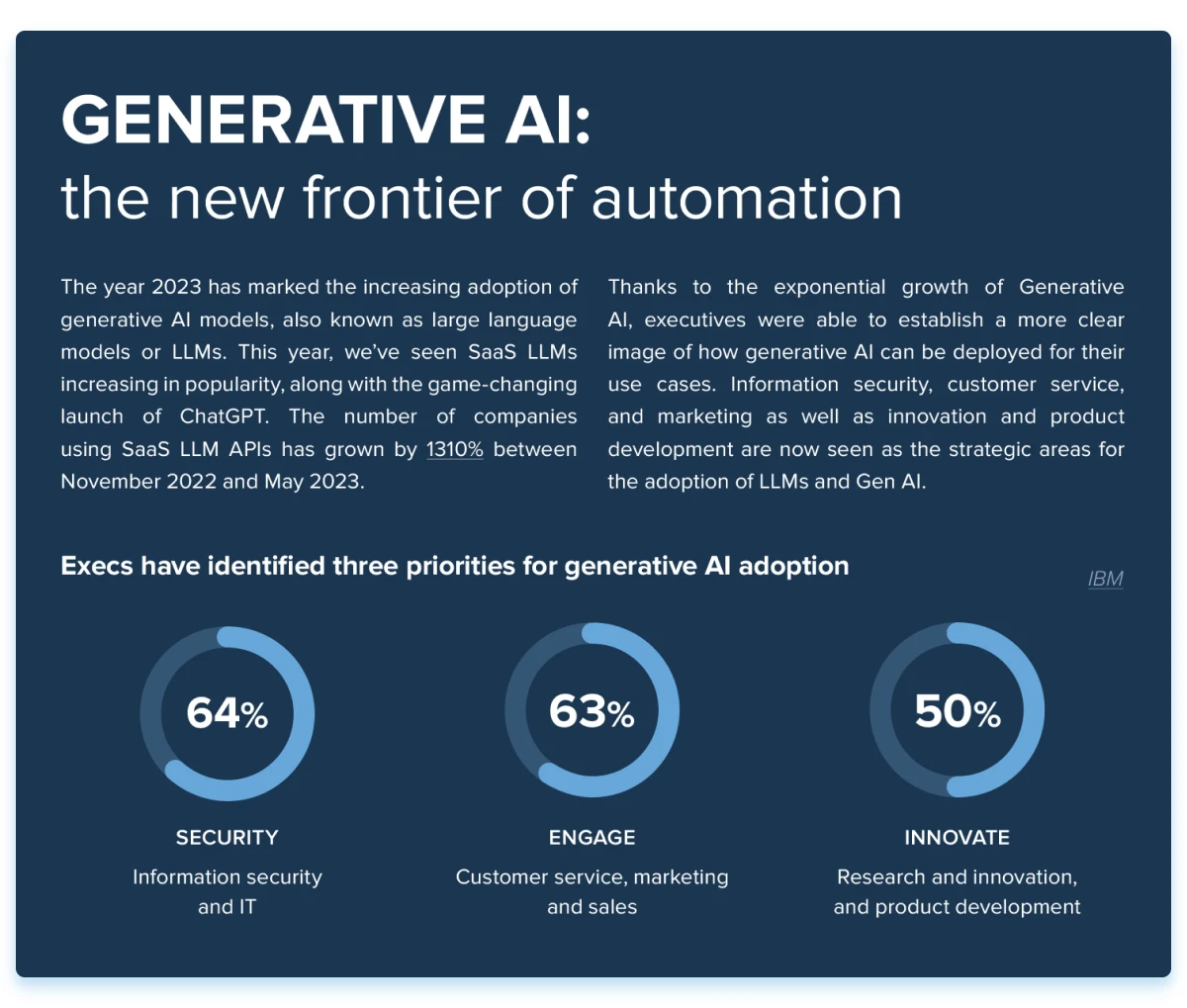
Generative AI use cases across industries
The effect of adopting generative AI technologies will differ based on the business function and industry.
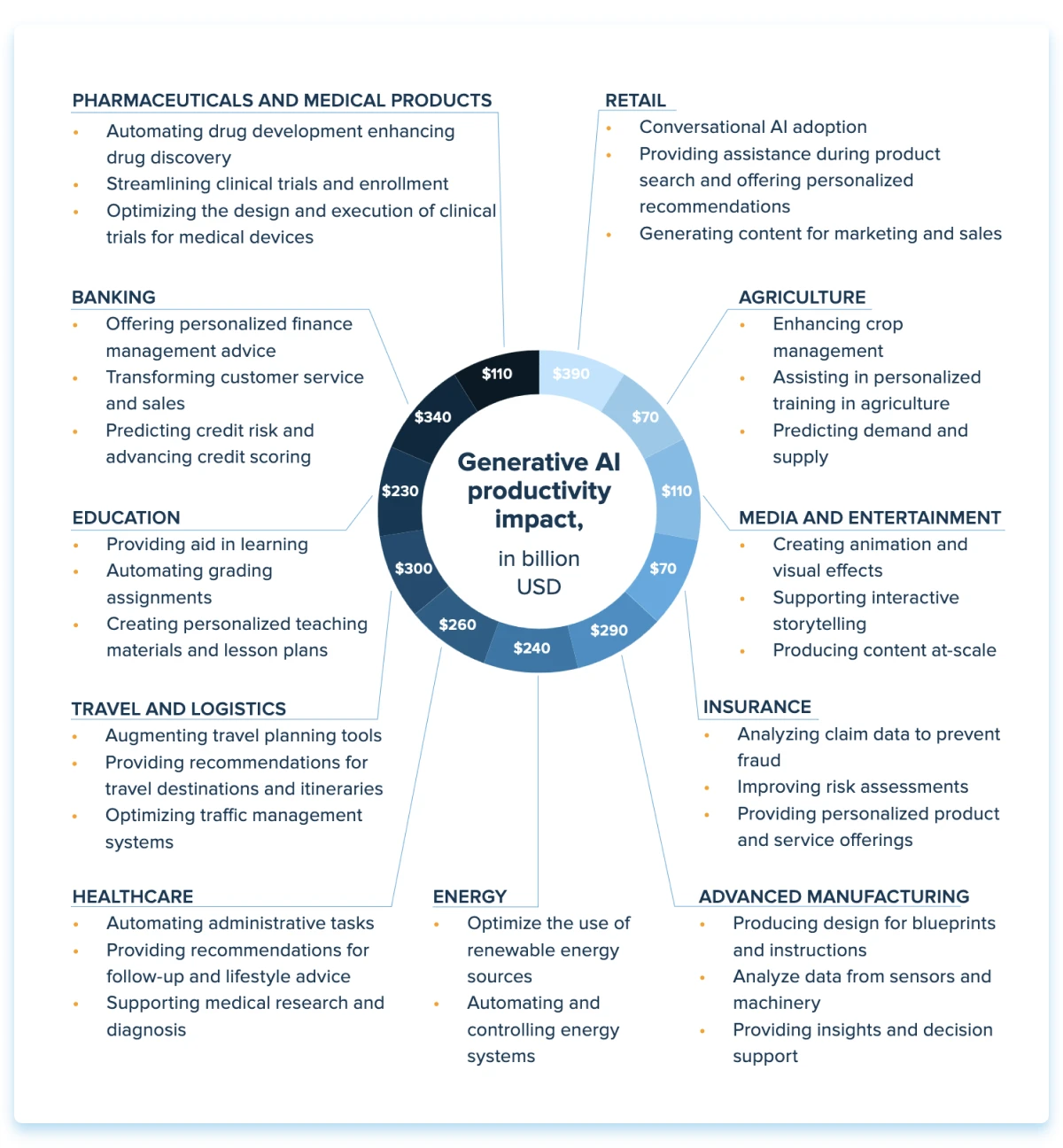
AI adoption by industry, accelerated
A few years ago, there was a wide AI gap among industries. Industries like tech were traditionally far ahead of other verticals, while finance and healthcare trailed behind due to stringent regulations and AI stigma. In 2023, the gap has tightened, making artificial intelligence a priority for healthcare, banking, and tech alike.
Loosening restrictions on the use of artificial intelligence technology also makes its adoption possible for industries that used to be left out of smart transformation. However, there is still enormous room for growth in AI invention across all industries and an enormous opportunity for those companies that can see it.
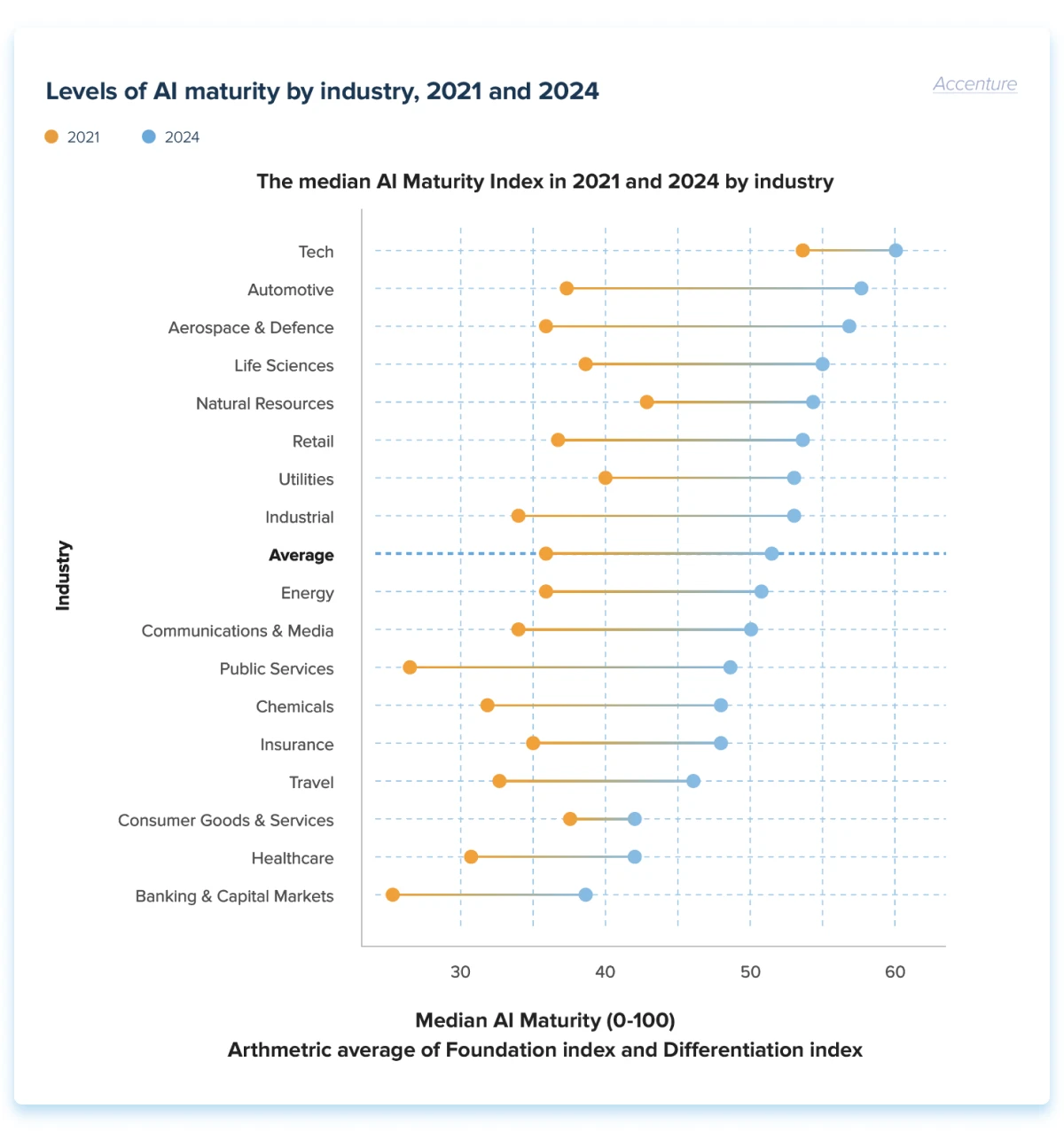
As of today, technology, automotive, and aerospace stand to professionalize and formalize their approach to AI faster than others – with the average maturity* index to approach 60 by 2024. Other innovation leaders such as retail and manufacturing are also expected to make a quantum leap to mature foundational AI capabilities.
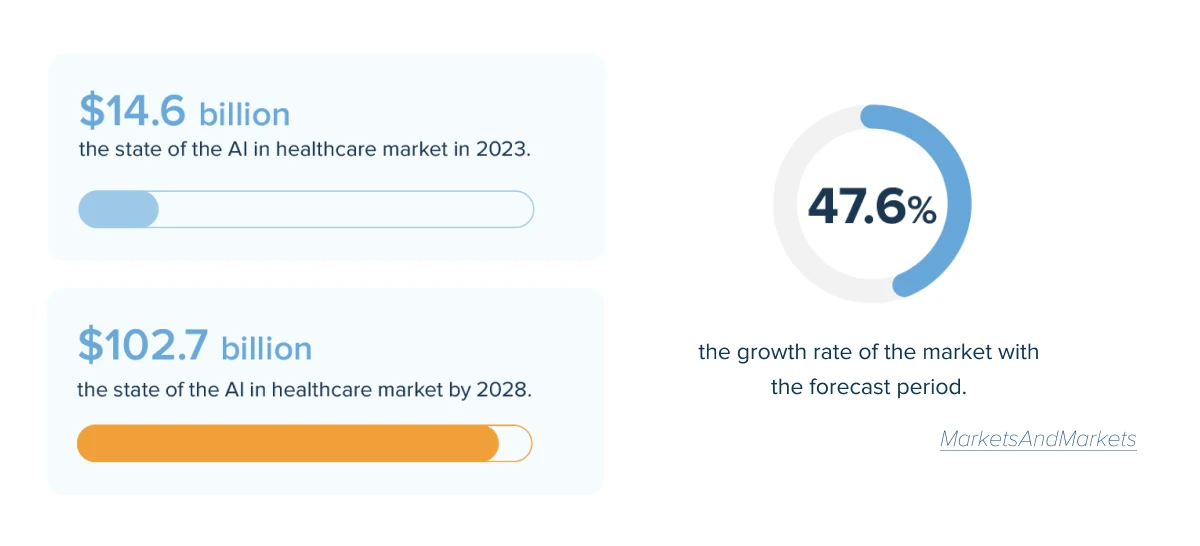
Regulation-heavy players are still cautious about going full-on with smart automation, yet are advancing fast into the field. In terms of AI investment, the focus areas with the most investment include medical and healthcare ($6.1 billion). It is followed by data management, processing, and cloud ($5.9 billion) and Fintech ($5.5 billion).
AI application matrix in healthcare
Three areas with the biggest AI potential:
- Supporting diagnosis and treatment decisions
- Clinical trials
- Imaging diagnostics (radiology, pathology).
Consumer benefits:
Smart algorithms can help enhance the accuracy and speed of diagnosis by monitoring and analyzing patient data and providing treatment. This, in turn, can lead to better patient outcomes, improved quality of life, and reduced healthcare costs. Generative AI can streamline administrative tasks, assist researchers in clinical trial planning, and offer more engagement to patients.
Industry gains:
Automation of time-consuming administrative tasks allows healthcare professionals to cut time spent on paperwork. More effective analysis and disease prevention help reduce the risk of illness and hospitalization, thus cutting the costs of healthcare.

Source: Unsplash
Market drivers:
- Increase in investments by pharma and MedTech companies into artificial intelligence systems
- Rising costs of healthcare and the need to optimize workflows
- Rising requirement for remote patient monitoring systems and data analysis.
Barriers to overcome:
- Lack of skilled AI workforce
- Ambiguous and evolving industry regulations
- Data privacy and security
- Lack of technological expertise.
Ready-to-go applications:
Tools to improve and streamline administration for insurers, payers, and providers.
Longer-term potential:
AI and robotics in healthcare (robot-assisted surgeries, robot doctors).
High-potential use case: Clinical trials
AI-supported patient recruitment allows researchers to find and enroll patients who meet the specific criteria for a trial. By analyzing large amounts of patient data and medical records, AI algorithms significantly speed up the recruitment process and ensure that the right patients are enrolled. Smart algorithms also support at-scale data analysis during clinical trials to identify patterns or correlations. This can help researchers better understand the effects of a new treatment.
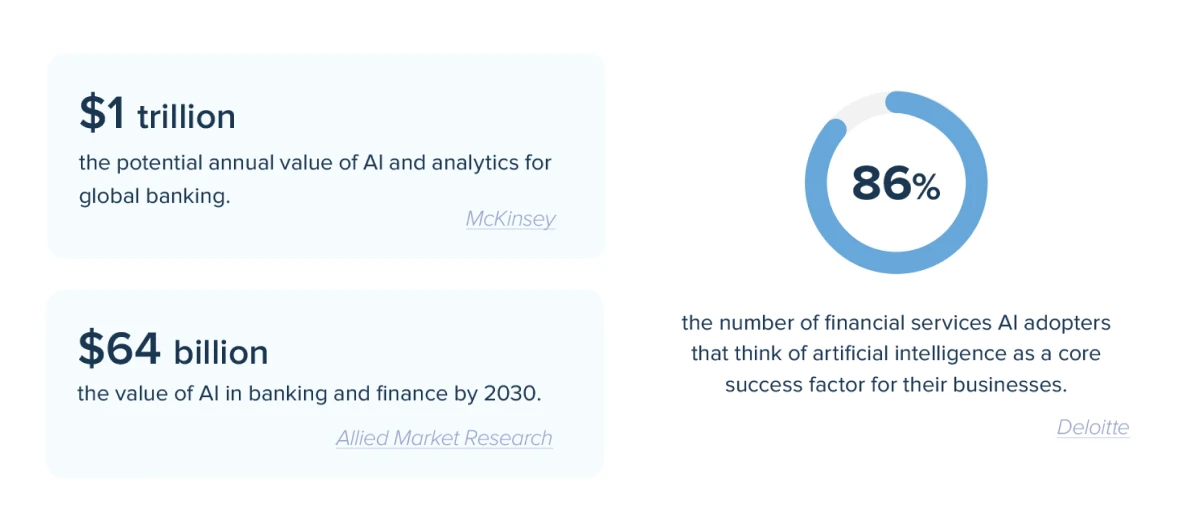
AI application matrix in banking and finance
Three areas with the biggest AI potential:
- Chatbots and virtual assistants
- Risk management compliance and security
- Personalized offers and customer retention
Consumer benefits:
Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by artificial intelligence provide instant answers and tailored advice to customers round-the-clock. This empowers consumers to make more informed financial decisions and get their issues resolved faster. Moreover, AI algorithms ensure higher security by detecting anomalies in transaction data.
Industry gains:
By implementing AI-enabled tools into their workflows, banks shorten support wait times, ease the strain on human workers, and scale up-selling and cross-selling activities. Using a smart decision management system helps financial services companies to prevent fraud and ensure compliance with relevant regulations. The speed of AI-supported analysis also allows banks to improve the accuracy and efficiency of KYC processes.
Market drivers:
- Rising demand for personalized financial services
- Growing adoption of smart technologies among leading financial institutions
- The growing availability and volume of data
- Skill gap and workforce adaptation.
Barriers to overcome:
- Security standards and regulatory requirements
- A weak core technology and data backbone.
Ready-to-go applications:
Tools to detect and prevent fraudulent transactions.
Longer-term potential:
Super apps with built-in digital identity, instant payment, and data-driven capabilities.
High-potential use case: Chatbots and virtual assistants
Virtual assistants and chatbots offer 24/7 assistance to customers, guiding them through simple transactions and helping them resolve basic issues. By automating these routine tasks, banks can free up their customer service representatives to focus on more complex inquiries, effectively reducing customer wait times.
Also, by analyzing historical customer data, a virtual assistant offers personalized budgeting or savings advice to a customer. This helps banks and finance service companies build stronger relationships with their customers.
AI application matrix in manufacturing
Three areas with the biggest AI potential:
- Predictive maintenance based on sensor data analysis
- Inventory management and forecasting
- Process optimization based on smart automation and analytics.
Consumer benefits:
Through intelligent inventory management and order processing systems, manufacturers can calculate with near-100% certainty when orders can be shipped and when they will arrive at their customers’ warehouses. Real-time visibility into equipment performance allows manufacturers to improve product quality and minimize the number of faulty products.
Industry gains:
By identifying and addressing issues early on, manufacturers reduce the number of defects in products, thus saving costs associated with recalls and returns. Through predictive maintenance, companies can increase production line availability, reduce maintenance costs, and prevent unplanned downtime.

Source: Unsplash
Market drivers:
- More complex decision-making processes due to the surge in digital information
- The need to optimize sustainability efforts in manufacturing
- Disruption in supply chains.
Barriers to overcome:
- Inability to pivot legacy applications and technology infrastructure
- Lack of interoperability
- Lack of universal industrial data.
Ready-to-go applications:
- Quality control with artificial intelligence
- Longer-term potential:
- Product conceptualization assisted by generative AI.
High-potential use case: Predictive maintenance based on sensor data analysis
Equipped with IoT, data analytics, and machine learning, companies can squeeze maximum intelligence from their sensor data to make data-driven decisions and optimize their maintenance strategies.
Predictive maintenance aims to identify early warning signs or patterns in the data that indicate a potential issue with the equipment. By detecting these patterns, companies can schedule maintenance or repairs before a breakdown occurs, minimizing downtime and reducing costs associated with emergency repairs.

AI application matrix in retail
Three areas with the biggest AI potential:
- Supply chain planning
- Customer support (chatbots, AI shopping assistants)
- Personalized shopping experience based on generative AI.
Consumer benefits:
For customers, AI-based improvements result in reduced shopping time and higher satisfaction thanks to personalized offerings tailored to their preferences. Also, customers can enjoy round-the-clock services as chatbots and shopping assistants can address their queries 24/7. Through accurate demand prediction, retailers can provide instant or same-day delivery.
Industry gains:
Smart algorithms can identify patterns and trends, enabling retailers to make data-driven decisions and tailor their offerings to meet customer demands. This can lead to more granular offering, better inventory management, and improved supply chain efficiency.
Market drivers:
- Evolving customer demands resulting from the availability of personalized and/or higher-quality AI-enhanced products and services.
- A growing number of distribution channels
- The need for supply chain optimization.
Barriers to overcome:
- Insufficient quality, volume, and accuracy of retail data and lack of tracking or data analytics
- Concerns about customer data
- Lack of skilled specialists
- Ready-to-go applications:
- Product and service recommendations for customers based on their purchase behavior.
Longer-term potential:
Avatar-based online shopping experience.
High-potential use case: Personalized shopping experience based on generative AI
Generative AI steps up personalization, making it more proactive, and allows companies to anticipate future customer behaviors and preferences. Through generative AI applications, retailers can generate personalized emails at scale, create smarter marketing journeys, and provide more personalized shopping experiences for customers.






