Nowadays we live in a world where around 2.5 quintillion bytes worth of data are generated each day. In the end, every business faces a problem in dealing with such volumes: besides being collected, it has to be processed and analyzed. The solution to this is Big data analytics, that transforms managerial choices through a data-driven revolution that opens up endless opportunities.
Using large datasets may help organizations find trends, gain an edge over others, and make informed decisions. Today Big data analytics adoption is the key to thriving in the age of digitization and ushering in a new era of prosperity.
What is Big data analytics?
Businesses may obtain a thorough insight into their consumers, market dynamics, and internal operations by examining a variety of data sources, such as customer interactions, data from social media, and operational indicators. By using these insights, firms may improve customer happiness and spur corporate growth by making well-informed decisions, adjusting strategies, and customizing their offers to match the demands of their customers.
The 3 V’s are often used when describing the term ‘Big data’:
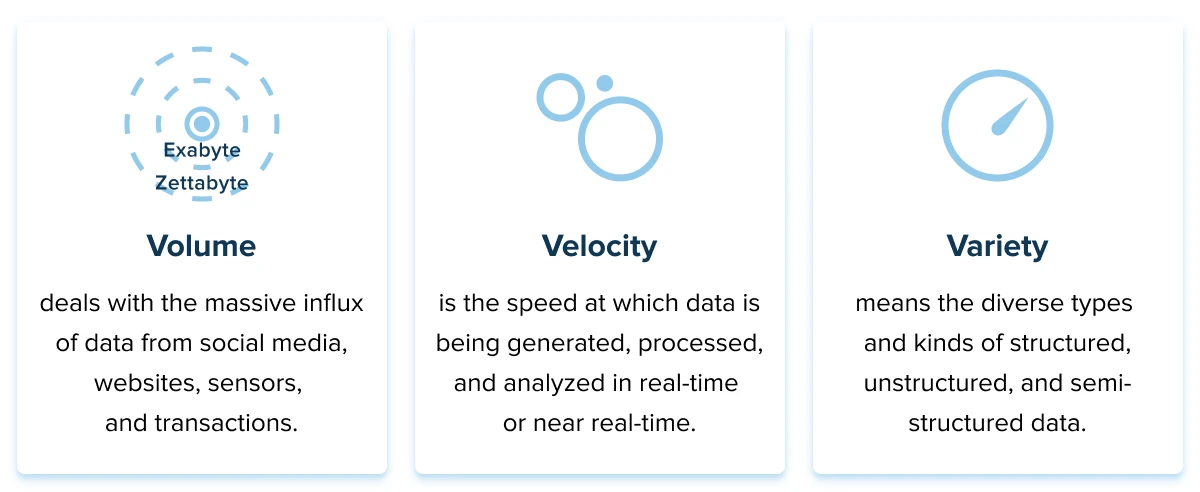
Companies that process Big data may hone in on other Vs as well, such as value, veracity, and variability. Value refers to the significance and usefulness of the insights derived from Big data. Veracity relates to the credibility, correctness, and trustworthiness of the data collected. Variability defines the dynamic nature of data, which can exhibit fluctuations, inconsistency, or changes over time.
How does it work?
Big data analytics entails several crucial processes that taken together make it possible to conclude enormous and intricate databases. Working with them involves the following steps:
Data collection
Gathering pertinent data from several sources is the first stage in the Big data analytics process. This can comprise semi-structured data from sources like log files or sensor readings, structured data from databases, and unstructured data from websites like social media or written content. The company’s internal systems, outside sources, alliances, and cooperative efforts can all provide the data.
Data storage
After being gathered, the data must be processed and stored in an appropriate architecture to enable successful analysis. Common storage options include data lakes and data warehouses. Data lakes store raw and unprocessed data in its original format, allowing for flexibility in data exploration and analysis. Data warehouses, on the other hand, are structured databases designed for optimized querying and analysis, with predefined schemas and indexing.
Data preprocessing
Raw data often requires preprocessing before analysis. In this stage, missing values are handled, duplicate or unnecessary entries are removed, and data formats are standardized. Preparing the data for analysis also entails putting it into an appropriate framework, such as converting unstructured text data into structured formats or aggregating data at the desired level of granularity.

Source: Unsplash
Data processing
It describes a way of applying a range of analytical methods to search for patterns, correlations, and trends in data. Descriptive analytics is a helpful tool in this strategy since it summarizes and presents data to help comprehend past activities. On the contrary, predictive analytics uses statistical models and machine learning to forecast future events based on existing information. Prescriptive analytics takes one step further by offering analysis and recommendations for enhancing future results through the use of prediction models.
Data visualization and reporting
The information gained from data analysis is often visualized and reported in a human-readable format. Charts, graphs, and dashboards are examples of data visualization tools that make complicated information easier to grasp quickly. Reporting tools make it possible to share findings with stakeholders, which promotes data-driven decision-making throughout the company.
Iterative process
We should keep in mind that Big data analytics is frequently an iterative process in which initial findings inspire more investigation and improvement. Additional data sources may be added, analytical methods may be modified in response to fresh findings, and specific business concerns may be addressed.
Big data use cases
A fifth of digital leaders believe they are leveraging data insights to increase revenue. Better corporate decision-making, risk detection, and mitigation, process and operation optimization, increased customer happiness, and insightful knowledge of industry trends and opportunities are just a few of the use cases for data analytics. Numerous sectors utilize diverse Big data analytics and business intelligence applications to attain commercial triumph by scrutinizing vast quantities of unorganized data to get practical understandings.
According to Forbes, around 87.8% of the companies have increased their investment in data in 2023. Some examples of Big data use cases among organizations include:
- Amazon, the biggest online retailer in the world, utilizes Big data to examine consumer data and activity, such as surfing and purchasing patterns, to customize each customer’s shopping experience.
- Netflix generates personalized content recommendations for its users based on their viewing preferences and history. This has led to higher user engagement and retention rates for the streaming platform.
- Apple finds out how people are using apps in real life and changes future designs to fit with customer preferences.
- Facebook also uses Big data to enhance the experience of their users.
See below for details on how real businesses benefit from Big data analytics.
Benefits of Big data
Big data development and analytics provide numerous benefits such as improved future outcomes and strategic advantages. However, it is not limited to these advantages only. Big data may be used by organizations of all sizes to obtain insightful information and make well-informed choices regarding their operations. For example, companies may use data analysis to better understand client preferences and create plans that will influence their business. Below, you can find the reasons why Big data analytics is important:
- Cost-cutting. Monitoring data also assists businesses in identifying areas where they may work more effectively to save money.
- Product development. Based on information gathered from customers’ requirements and preferences, creating and promoting new goods, services, or brands is considerably simpler. Businesses may also better analyze product viability and stay on top of trends with the aid of Big data analytics.
- Strategic business choices, such as supply chain, and cost optimization, may be made more quickly and effectively by firms with the capacity to continuously evaluate data.
- Customer experience. Businesses can acquire crucial details about consumer preferences, purchase trends, and the variables impacting their decisions. With the use of E-commerce analytics, businesses may identify new market niches, concentrate their marketing efforts, and comprehend their target audience more thoroughly.
- Tailored ads. Users may benefit from engaging in targeted ad campaigns that are both personally and broadly appealing when they are created with the help of personalization data from sources including prior purchases, interaction patterns, and product page viewing histories.
- Risk management. Businesses may detect hazards and create proactive methods to mitigate them ahead of time by looking at data patterns.
- Real-time intelligence. Organizations can quickly examine large amounts of real-time data in a variety of forms and sorts from several sources.
- Intelligence in real time. Large volumes of real-time data in a variety of forms and kinds, from several sources, may be swiftly analyzed by organizations.
Potential сhallenges
While Big data analytics offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that organizations need to address. Here are some key Big data problems that businesses can face:
Volume, variety, and velocity
Managing an enormous amount of data is a major difficulty in Big data analytics. Organizations require scalable processing and storage solutions to effectively store and analyze massive datasets as the volume of data grows rapidly. Because data is created and analyzed so fast, real-time analytics face problems. To get timely insights and make informed decisions, organizations need to be able to gather, process, and analyze streaming data in practically real-time.

Source: Unsplash
Big data is made up of several kinds of data, such as semi-structured, unstructured, and structured data. It might be difficult and necessitate the use of specialist tools and procedures to analyze and integrate diverse data sources in different formats.
Solution: Specific tools like Apache Hadoop, NoSQL databases, Spark and Tableau can help you collect, process, cleanse, and analyze Big data.
Data privacy and security
As more sensitive data is being gathered, worries about security and privacy are becoming increasingly widespread. Three of the biggest issues in Big data analytics are protecting data from unwanted access, making sure that data protection laws are followed, and preserving data privacy.
Solution: Integrating role-based access controls, multi-factor authentication, and encryption techniques will protect data both at rest and in transit.
Infrastructure and technology
It might be difficult to implement the technological stack and infrastructure needed for Big data analytics services. Organizations must invest in frameworks for handling data, analytical tools, and scalable and dependable storage solutions. It can be challenging to build and maintain such infrastructure while ensuring it integrates and is compatible with current systems.
Solution: The good news is, according to Brimco, that over 60% of all corporate data is in cloud storage. So investing in scalable and resilient cloud services can be helpful when handling the increasing volume and velocity of Big data.
Lack of talent
Some companies are having trouble filling the gaps due to a possible shortage of internal analytics capabilities and the high cost of acquiring skilled data scientists and engineers. But this step is very crucial when it comes to Big data analytics integration as it defines the success of the business.
Solution: A reliable IT vendor will ensure that Big data analytics services are integrated correctly.

Source: Unsplash
Regulatory compliance
Legal and regulatory obligations must be negotiated by organizations while gathering, storing, and evaluating data. Complying with industry rules, data governance frameworks, and data protection legislation increases the intricacy of Big data analytics projects.
Solution: Organizations must stay informed about the evolving data protection and privacy regulations within their industry and geographical region.
Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach, investing in the right technology and infrastructure, fostering a data-driven culture, and ensuring proper data governance practices. It is crucial for organizations to have a clear understanding of these challenges and develop proactive strategies to overcome them to fully leverage the potential of Big data analytics.
To draw the line
As we move forward in this data-driven era, the value of Big data analytics will continue to grow. This advanced technology has evolved into a vital tool for organizations seeking to thrive in a rapidly evolving and data-centric business landscape. Many businesses have already discovered the benefits of acquiring as much data as they can. But merely collecting and maintaining large data is insufficient; you also need to put it into use.
Businesses that use data to their fullest potential will be more likely to recognize new possibilities, adjust to shifting market dynamics, and outperform rivals. By addressing the challenges and embracing the potential of Big data analytics benefits, businesses will be able to unlock new insights, drive innovation, and achieve sustainable growth in today’s data-centric world. The adoption of Big data analytics is no longer an optional strategy but a fundamental necessity for businesses that aspire to stay relevant and competitive in the digital era.
FAQ
-
To put it simply, it is a process of scrutunizing data and sorting it out in order to extract useful information out of it. Organizations can use it to solve a myriad of problems and boost their business-related outcomes. Usually it is done for simplification of accounting, market trends detection, clients preferences check and progress measurement.
-
Utilized in many fields, some examples of Big data are:
- Personalized marketing. Thanks to Big data analytics, companies target specific audiences with tailored offers and incentives, increasing consumer engagement and loyalty.
- Logistics. Businesses may improve the performance of their supply chains worldwide by seeing possible issues and acting proactively to prevent them with the use of real-time data.
- Banking and finance. Banks surveil spending habits and other activities, identifying any unusual movements or irregularities that may be signs of fraudulent transactions.
-
Plenty of companies in all kinds of industries use Big data. The blue-chip companies that use big data are Amazon, Apple, Netflix, Facebook and others. They leverage Big data analytics in order to draw in more clients, boost customer satisfaction, adjust supply to demand and create better marketing campaigns.
-
The primary purpose is to provide a report that will be useful for business, whether it’s about market trends, clients interests dynamics or overall profitability. Businesses utilize Big data analytics due to the need to stay afloat and optimize their operations as it gives companies all the necessary resources and knowledge.
-
It brings many benefits to the table, some of them are:
- increased efficacy,
- future trends prediction,
- fraud detection,
- research and innovation fostering,
- risk management,
- customer sentiment analysis,
- prize optimization,
- targeted ads and many more.
As a result, the business obtains better flexibility and faster reactions to ever-changing market situations, standing out from its rivals.
-
Leveraging this technology can make business forget about many pain points. The most common problems that big data analytics can tackle for you are:
- market unpredictability,
- impossibility of making up plans,
- unprofitability,
- huge costs,
- low client loyalty rate and other issues.



